* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Behavioral Theories of Learning
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral economics wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
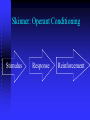
Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice Chapter 5 Behavioral Theories of Learning This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: • any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; • preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; • any rental, lease, or lending of the program. ISBN: 0-205-31479-1 “You often learn when you don’t intend to learn, and you often teach when you don’t intend to teach” What is Learning? A Change in Behavior as a Result of Experience Examples of Learned Behaviors Non-Examples (Unlearned Behaviors) Intentional Learning Unintentional Learning Behavioral Theories of Learning Emphasize Observable Behavior Pavlov: Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus Unconditioned Response Neutral Stimulus Conditioned Stimulus Conditioned Response Give an Example of Classical Conditioning in a Classroom Setting Can You Identify the Components in Classical Conditioning Examples? Unconditioned Stimulus Unconditioned Response Conditioned Stimulus Conditioned Response Thorndike: The Law of Effect “…the consequences of one’s present behavior play a crucial role in determining one’s future behavior.” (p. 144) B.F. Skinner Skinner: Operant Conditioning Stimulus Response Reinforcement Principles: Reinforcement A Consequence That Strengthens a Behavior Repeat: Reinforcement Strengthens a Behavior If the Frequency of a Behavior Increases After a Consequence, the Consequence is a Reinforcer There Are Several Types of Reinforcers Principles: Reinforcers Primary and Secondary Positive and Negative Free and Contingent (Premack Principle) Intrinsic and Extrinsic Continuous and Intermittent (Schedules) Principles: Punishment A Consequence That Weakens a Behavior Repeat: Punishment Weakens a Behavior If the Frequency of a Behavior Decreases After a Consequence, the Consequence is a Punisher There Are Several Types of Punishers Principles: Punishers Presentation and Removal Time Out Effectiveness of Punishment Can You Distinguish Between the Different Types of Behavioral Consequences? Positive Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement Punishment Principles: Shaping Reinforcing Approaching Final Behavior Breaking Task into Parts Using in Classroom Principles: Extinction Behavior That Is Not Reinforced Will Weaken Extinction Burst Considerations In Classroom Management Social Learning Theory: Bandura Modeling Phases of Observational Learning Behavioral Principles in the Classroom Avoid Overjustification Effect - Zimbardo Guidelines on the use of Rewards - Deci Give Rewards to Inform Rewards Should Not Be Used to Manipulate Reward for Academic Performance Reward Incentives Should Be Inconspicuous Bribes Weaken Intrinsic Motivation