* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plant, animal, and Fungus
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
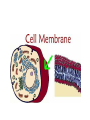
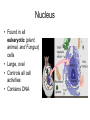
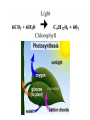
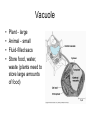
Cell Organelles and Processes Cell Wall • Is found in plant or fungus cell , not animal • Outer layer • Made of cellulose • Supports and protects cell • Allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass into and out of cell Cell Membrane • Found in both plant and animal cells – Plant - inside cell wall – Animal - outer layer • Selectively permeable (filter) • Controls movement of materials in/out of cell Nucleus • Found in all eukaryotic (plant, animal, and Fungus) cells • Large, oval • Controls all cell activities • Contains DNA Cytoplasm • Found in all cells • Clear, thick, jellylike material • Supports /protects cell organelles Mitochondria • In all cells • Bean-shaped with inner membranes • Breaks down sugar molecules into energy –Called “Power Plants” of the cell Chloroplasts • Found in plant, not animal cells • Green, oval containing chlorophyll (green pigment) • Uses energy from sun to make food for the plant (photosynthesis) Vacuole • • • • Plant - large Animal - small Fluid-filled sacs Store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts of food) Plant or Animal? • Plant and animal cells are similar in structure but there are differences. • This is an illustration of a plant cell and animal cell • Plant cells have a cell wall, animal cells do not. • Plant cells have chloroplasts, animal cells do not. • Plant cells generally have a more rectangular shape because the cell wall is more rigid. • Animal cells have a round or irregular shape because they do not have a cell wall. • Both plant and animal cells contain a cell membrane. Comparing a Cell to a Factory Turn your books to Page 20 (Book C) End of Cell Structure Notes Diffusion and Osmosis • Diffusion - the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration, to areas of low concentration. When the molecules are even throughout a space - it is called EQUILIBRIUM • Osmosis - the diffusion of water (across a membrane) • Like other molecules water will move until it’s evenly spread on both sides of the membrane. • For example: salt is a solute, when it is concentrated inside or outside the cell, it will draw the water in its direction. This is also why you get thirsty after eating something salty. • Suppose an animal or a plant cell is placed in a solution of sugar or salt in water. • If the medium is hypotonic — a dilute solution, with a higher water concentration than the cell — the cell will gain water through osmosis. • If the medium is isotonic — a solution with exactly the same water concentration as the cell — there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane. • If the medium is hypertonic — a concentrated solution, with a lower water concentration than the cell — the cell will lose water by osmosis. • So basically, if a cell is put in a solution which is more concentrated than its own, then it will shrivel up, and if it is put in a solution less concentrated than its own, the cell will expand and burst.