* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell membranes - the Redhill Academy
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
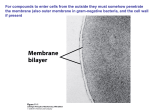
Cell membranes Links to GCSE Structure of animals & plant cells Diffusion Sensitivity Hormones Week 3 • State that plasma (cell surface) membranes are partially permeable barriers. • Outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Membranes play a role in: Separating cell contents from the external environment Separating cell components from cytoplasm Cell recognition & signalling Holding the components of some metabolic pathways in place Regulating the transport of materials into & out of cells Phospholipids A) Phospholipid molecule enlarged B) Layer of phospholipids at the surface of water Week 3 A phospholipid bilayer © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Through an electron microscope 7-10nm Week 3 • Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure. • Describe the roles of the components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids, proteins and glycoproteins. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original The ‘Fluid Mosaic Model’ of cell membranes, Singer & Nicholson Making a model of the ‘Fluid Mosaic Model’! You will be provided with a range of materials to help you construct a large physical model of ‘The Fluid Mosaic Model of Membranes’ Your model should contain the key structures present in a cell membrane You will be expected to present your model and explain the functions of ALL of the key structures You have the remainder of this lesson and only one more for preparation, so will have to work on this outside of lessons (i.e. HOMEWORK!!) Week 3 • Outline the effects of changing temperature on membrane structure and permeability. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 3 • Explain the term ‘cell signalling’. • Explain the role of membrane-bound receptors as sites where hormones and drugs can bind. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Key definitions Cell signalling: cells communicate with one another by signals. Many molecules act as signals –some signal during processes taking place inside cells; others signal from one cell to others. Cytokines are an example of cell signals. Chemicals & receptor effects Insulin Medical drugs such as anti histamines/ beta blockers (high blood pressure), L dopa (schizophrenia) etc Botox (botulism toxin!) HIV entry into cells Membrane transport Links to GCSE Diffusion Osmosis Week 4 • Describe and explain what is meant by passive transport (diffusion and facilitated diffusion). • Describe the role of membrane proteins in passive transport. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 4 (a) Simple diffusion (b) Facilitated diffusion using a channel protein (c) Facilitated diffusion using a carrier protein © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Key terms DIFFUSION: the movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration (of that molecule) down a concentration gradient. KINETIC ENERGY: movement energy possessed by molecules. EQUILIBRIUM: no OVERALL movement of molecules Week 4 • Describe and explain what is meant by active transport. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 4 • Describe and explain what is meant by endocytosis and exocytosis. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 4 • Explain what is meant by osmosis, in terms of water potential. • Recognise and explain the effects of solutions of different water potentials on plant and animal cells. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 4 Osmosis and membrane © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 4 Plant and animal cells in solutions of high water potential - before and after © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 4 Plant and animal cells in solutions of low water potential - before and after © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original • State that plasma (cell surface) membranes are partially permeable barriers. • Outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. • Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure. • Describe the roles of the components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids, proteins and glycoproteins. • Outline the effects of changing temperature on membrane structure and permeability. • Explain the term ‘cell signalling’. • Explain the role of membrane-bound receptors as sites where hormones and drugs can bind. • Describe and explain what is meant by passive transport (diffusion and facilitated diffusion). • Describe the role of membrane proteins in passive transport. • Explain what is meant by osmosis, in terms of water potential. • Recognise and explain the effects of solutions of different water potentials on plant and animal cells.