* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Semester 1 Exam
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
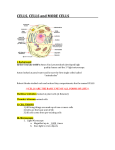
SEMESTER 1 EXAM- STUDY GUIDE By: Vicky Zang, Julia Malachowski, Ashley Liu, and Muskaan Uppal What are the levels of classification from kingdom to species? Kingdom Phylum Class Family Order Genus Species What is binomial nomenclature? Two- part scientific name (Genus species) What does MRS. GREN stand for? Movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, excretion, nutrition What are the five kingdoms? Animal Plant Fungi Protist Moneran What are characteristics of organisms within each of the 5 kingdoms? (multicellular or unicellular) Animal- multicellular Plant- multicellular Fungi- multicellular Protist- unicellular Moneran- unicellular What is a dichotomous key? A key that scientists use to determine the classification of an organism Name five things that scientists use for classification Behavior and physical appearance Method of reproduction, locomotion, diet and habitat Cell and DNA analysis What are the characteristics of insects? Wings Exoskeleton 6 Legs 3 Body Parts Simple/Compound Eyes Metamorphosis Antennae Jointed Legs What is the most diverse and populous insect order? Beetles How do insects make sounds? Tymbals Spiracles Stridulation Snap Mandibles Tap Body Parts On Surface Name the three different mouthparts that insects can have Sponging Piercing/ Sucking Siphoning Name the three different types of metamorphosis Molting- shedding skin Incomplete- egg, nymph, adult Complete- egg, larva, pupa, adult Who was Robert Hooke? He observed cork cells; coined the term “cell” Who was Anton Van Leeuwenhoek? He observed bacteria and protists. Who was Zacharias Janssen? He looked at the first compound microscope. How do you get total magnification? Eyepiece x Objective lens How do you properly hold a microscope? Put one hand on the body tube (arm) and one hand on the base. What is the stage? This is where the specimen rests What is the eyepiece? The lens that you look through What are the objective lenses? They are attached to the revolving nose piece combined with the power of the ocular lens to create the magnified image Name the levels of organization from cell- organism Cell Tissue Organs Organ System Organisms What are the two types of cells (body/ sex cells)? Somatic and gametes What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus but prokaryotic cells do not List differences between plant and animal cells Cell wall- plant Chloroplasts- plant Vacuole size- plants have one big one, animal have smaller ones What is cytoplasm? A jelly-like substance that contains organelles What is the function of the nucleus? It is the control center for all activities What is the nucleolus? It contains genetic material, it also makes ribosomes, and is a dark colored organelle in the nucleus What is the nuclear membrane? A membrane that controls movement of materials in and out of nucleus What are chromosomes? It is DNA inside the nucleus What is endoplasmic reticulum? An internal delivery system that aids in making proteins connects cell membrane to nuclear membrane What are ribosomes? Tiny spherical bodies that help make proteins. They are found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. What are mitochondria? The site of cellular respiration. It breaks down sugar molecules to release energy. What are vacuoles? Act as a storage area for food, minerals, and waste. In plants they are very large but in animals they are smaller. What is the cell membrane? It separates the cell from other cells. Allows molecules to pass through. What is the function of the cell wall? Supports and protects the cell What is chloroplasts? An organelle in a plant that uses energy from the sun to make food for the plant (photosynthesis) What are lysosomes? Organelles that break down larger food molecules into smaller molecules. What are centrioles? Organelles that play a role in cell division. What are golgi bodies? Organelles that package and distribute materials throughout the cell. What is Diffusion? It is the movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration What is Osmosis? Diffusion of water molecules What is active transport? The movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy What is photosynthesis? The process by which a cell captures energy in sunlight and uses it to make food What is respiration? The process by which cells obtain energy from glucose What is the order of the scientific method and what takes place in each step? 1. Research/ Background information 2. State your purpose/ problem question 3. State your hypothesis/ make a logical prediction based on prior knowledge 4. Develop your procedure 5. Collect and record data (numerical and observable) 6. Analyze your results 7. Draw conclusion What is the independent and dependent variable? Independent variable- the factor you control Dependent variable- what you are testing/ measuring/ observing What are the experimental and control group? Experimental group- the testing group Control group- the group used for comparison What are controls? Controls- what is kept constant throughout the experiment GOOD LUCK!