* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Chromatophore wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
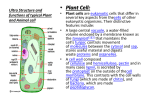
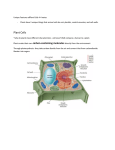
Cell Structure and Function 3 Things Plant Cells Have And Animal Cells Don’t! 1. Cell Wall Cell Wall -ALL Cells have a Cell membrane, but plant cells ALSO have a Cell Wall -It is made of cellulose -It gives shape, support, and structure to the plant cell 2. Large Vacuole Large Vacuole -the large vacuole is very similar to a lysosome in an animal cell -it contains enzymes and stores water and sometimes even poisons -it is the largest plant cell structure 3. Plastids Plastids -plastids are specialized structures that can help make food or store important pigments or other substances -three types of plastids are: chloroplasts – contain cholorphyll and help with photosynthesis (green) chromoplasts – contain pigments such as oraange (carotene), yellow (xanthophyll), and various reds leukoplasts – help plants store starch (white)