* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Reproduction
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
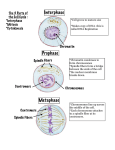
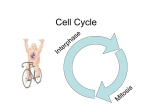
Cell Reproduction Chapter 8 Chromosomes Vs. Chromatin Chromosomes Chromatin Think of it like Cookies! Chromatin MAKES Chromosomes Our cells are constantly needing to replace themselves. For example, when we get a paper cut or any kind of cut, those cells need to be replaced. Also, cells in your stomach lining constantly need to be replaced, and even bone marrow cells. Cell Division: What is it? The Cell Cycle is a sequence of separate Division periods of __________ & __________ Growth The period where the cell grows in size, metabolizes, and spends a majority of its life is _______________ INTERPHASE Also, during this period, the chromosomes are duplicated to prepare for cell division. ___________ The period where the cell undergoes nuclear division and creates 2 daughter cells is called ____________ MITOSIS Each daughter cell contains a Complete ____________ set of the parent cell’s chromosomes. 75% of a cell’s life is spent in Interphase Which phase of the cell cycle takes the longest? Copies its chromosomes G1 S G2 “Checkpoints” = stop & go-ahead signals to regulate the cycle Regulatory molecules, usually enzymes (protein kinases) To become active kinases need a cyclin to trigger them Often called “Cdks” (cyclin-dependent kinases) PROPHASE The first phase = ____________ This is the ________ longest phase (OF MITOSIS) During this phase, chromatin coils to form visible _____________ chromosomes Each chromosome is made up of ___ 2 sister chromatids and are held together by a __________ centromere *Remember: The chromosomes are Interphase duplicated in ____________ to prepare for cell division The TWO together are sister chromatids One Chromatid Duplicated Chromatid nuclear envelope starts In addition, the ________ to disappear and the __________ nucleolus disintegrates. centrioles In animal cells, ___________ migrate to opposite ends of the cell and ________ spindle fibers ________ begin to form. In plant cells _______ Spindle _______ fibers form without centrioles. METAPHASE The Second Phase = _____________ • The chromosomes begin to line up along the _________ of the cell Equator attach to the • The spindle fibers _______ centromeres. • Each chromatid has its own spindle fiber attached The Third Phase = ____________ ANAPHASE This marks the ___________ separation of sister chromatids. The centromeres ______ and the split ______ sister ___________ chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell by shortening spindle fibers TELOPHASE The Fourth Phase = ______________ daughter cells start to Here two distinct _________ form. chromosomes unwind, the In addition, the _____________ break down, the _________ nucleolus spinder fibers ______ envelope reappears, a new nuclear __________ membrane begins forms, and a new double __________ to form between the two nuclei. Cytokinesis cytoplasm the division of ____________ Toward the end of telophase in animal cells, the plasma membrane _______ pinches in along the equator cell _________ membrane forms In plant cells, a ____ around each cell and new cell ______ wall form on each side of the cell plate until separation is complete. Can you identify any of the stages? Now the cells are separated, they will continue in the cell cycle and enter __________ interphase