* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
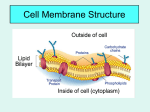
Gateway Biology Content Review Biological Systems Human Systems and Basic Life Functions Human Systems and Basic Life Functions Human Systems and Basic Life Functions System functions Cell Membrane (Plasma membrane) – Surrounds cell – Selective barrier – Controls what substances enter and exit the cell Homeostasis Maintaining a constant and stable environment inside of an organism Examples – Breathe in oxygen – Breathe out carbon dioxide – Eat Food Energy Building Blocks – – – – Eliminate Waste Maintain Temperature Blood pH Blood sugar How does each of the following organs, systems, or responses function in maintaining homeostasis? – – – – – – – – – – – – Kidneys Cardiovascular System Shivering Sweating Sunning Buffers in our blood Roots on a plant Leaves on a plant Digestive System Mitochondria Lysosome Stomach – Kidneys- filter waste out of blood to make urine – Cardiovascular System- transports nutrients & remove gaseous waste from body – Shivering-warm body – Sweating-cool body – Sunning– Buffers in our blood-protect against large changes in pH in blood – Roots on a plant-absorb nutrients and water – Leaves on a plant-trans-respiration, photosynthesis – Digestive System- breaks down food to provide Energy for body – Mitochondria- organelle uses glucose to make ATP (energy for cell) – Lysosome-organelle engulfs waste for cell – Stomach-aids in digestion Cellular Transport Materials Transported into a cell: – – – – – – – Nutrients Water Sugar (carbohydrates) Ions Amino Acids Fats Oxygen Materials Transported out of a cell: – – – – – Waste Carbon Dioxide Proteins Sugar Hormones Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Active Transport – Requires Energy (ATP), particles move from a lower to higher concentration. – Uses Transport Protein Endocytosis Exocytosis Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Passive Transport – Does not require energy – Particles move from high concentration to low concentration. – Works to reach equilibrium Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Passive Transport – Diffusion Movement of particles through the membrane down a concentration gradient http://www.indiana.edu/~phys215/lecture/lecnotes/diff.html Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Passive Transport – Osmosis Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Passive Transport – Facilitated Diffusion Movement of particles through a cell membrane by means of a transport protein. Down the concentration gradient Does NOT require energy. Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Osmosis – Movement of water – Water makes up about 70% of the cell and is required for transport of food, nutrients, and waste throughout the body. – Water moves from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution. Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Osmosis – These are relative terms used to compare two solutions Hypotonic Solution: Lower solute concentration Hypertonic Solution: Greater solute concentration Isotonic Solution: Equal solute concentration Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Osmosis – Animal Cells need to be surrounded by an isotonic solution Animal cells in a hypotonic solution gain water and will swell and burst Animal cells in a hypertonic solution lose water and will shrivel Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Osmosis Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Osmosis – Plant Cells need to be surrounded by a hypotonic solution. Plant cells in an isotonic solution become flaccid/ limp Plant cells in a hypertonic solution lose water undergo plasmolysis Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Endocytosis – “Cell eating” – A cell takes in macromolecules or other substances when regions of the plasma membrane surround the substance, pinch off, and form a vesicle within the cell. Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane Exocytosis – A cell secretes macromolecules –waste, hormones, neurotransmitters, etc. Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane- PRACTICE 1. An animal cell is placed in a hypertonic solution; what will happen to the cell? – Lose water, shrivel 2. A plant cell contains a solute concentration of 0.5M; in what direction will water move if the cell is placed in a 0.2M solution? – Into the cell 3. What term best describes the process by which a drop of food coloring over time spreads out uniformly through a beaker of water? – diffusion Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane- PRACTICE 4. In the diagram, what will be the direction of net water movement across the semi-permeable membrane? To the left 7.5M NaCl 5.7M NaCl