* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocytosis - Cloudfront.net
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
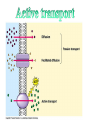
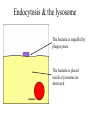
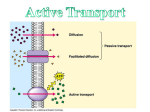
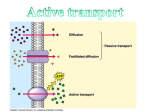
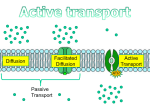
Active Transport • Defined: Molecules move from a LOW to a HIGH concentration • ATP energy needed to fight diffusion – ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate • ATP activates pumps (see animation) Endocytosis • Endocytosis: Process in which the plasma membrane takes in substances (2 types) – 1) Phagocytosis: when a cell engulfs a solid particle – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way Endocytosis & the lysosome The bacteria is engulfed by phagocytosis The bacteria is placed inside a lysosome are destroyed Exocytosis • Defined: Process when substances are expelled from the cell • Proteins, nutrients, and waste exit by exocytosis • Vesicle carry & release objects through the plasma membrane Contractile vacuole of a Paramecium As water enters this cell by diffusion, it is immediately pumped out to prevent bursting Kobe Kuiz 1) How area active and passive transport different? 2) Which molecule powers active transport? 3) How are endo- and exocytosis similar? Different? 4) Which cell part controls active transport?