* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eukaryotic Transcription
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
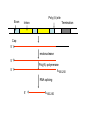
Eukaryotic Transcription Eukaryotic Transcriptional • Transcription control is the most important mode of control in eukaryotes. • Three RNA polymerases: – RNA Polymerase I: synthesis of pre-rRNA, which is processed into 28S, 5.8S, and 18S rRNAs – RNA polymerase III: synthesis of tRNA, 18 S rRNA, and small, stable RNAs – RNA polymerase II: synthesis of mRNAs and four small nuclear RNAs that take part in RNA splicing Eukaryotic Transcriptional • The main purpose is the execution of precise developmental decisions (irreversible). • Cis-acting control elements are located many kb away from the start site. • Promoter region is poorly characterized. TATA box About 25-35 bp upstream of the start site 5’ +1 TATAAA -34 to -26 mRNA start Well-defined transcription start Initiator • Instead of a TATA box, some eukaryotic gene contain an alternative promoter element, called an initiator. • Initiator is highly degenerative. +1 5’ Y Y A N T/A Y Y Y Y = pyrimidine (C or T) N = any CpG island • Genes coding for intermediary metabolism are transcribed at low rates, and do not contain a TATA box or initiator. • Most genes of this type contain a CG-rich stretch of 2050 nt within ~100 bp upstream of the start site region. • A transcription factor called SP1 recognizes these CGrich region. • Gives multiple alternative mRNA start sites. ~100 bp CpG island mRNA Multiple 5’-start sites Enhancers • Located several Kb away from the start site. • Usually ~100-200 bp long, containing multiple 8- to 20-bp control elements. • Cell-type specific • Direction-less (invertible) +1 Enhancer Enhancer Promoter Proximal Elements • • • • Occur within ~200 bp of the start site. Contain up to ~20 bp. Cell-type specific Invertible +1 Promoter Proximal element A hypothetic mammalian promoter region Promoter Proximal Element +1 Enhancer Enhancer -10~-50 Kb -200 TATA -30 Intron Exon Enhancer +10~50 Kb A hypothetic yeast promoter region +1 Enhancer TATA ~-90 mRNA processing Poly (A) site Exon Cap Intron Termination transcription 5’ The 5’-Cap is added to Nascent RNAs (pre-RNAs) shortly after initiation by RNA polymerase II. Pre-mRNAs are associated with hnRNP (heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles) proteins containing conserved RNA-binding domains Poly (A) site Exon Intron Termination Cap 5’ Cap endonuclease 5’ 5’ Poly(A) polymerase A100-250 Pre-mRNAs are cleaved at specific 3’ sites and rapidly polyadenylated Cleavage and polyadenylation Poly(A) signal Poly(A) site 5’ AAUAAA G/U rich Pre-mRNA 5’ AAUAAA AAAAAA100-250 Poly (A) site Exon Intron Termination Cap 5’ endonuclease 5’ Poly(A) polymerase A100-250 5’ RNA splicing 5’ A100-250