* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download albinism - whushguh
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
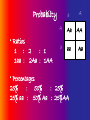
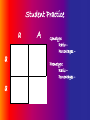
ALBINISM Greer Manton, Sydney Gilbert & Monica Starbinski 2/1/10 – Period 2 Please be respectful during this PowerPoint. The photos you may see today are unlike many others. Keep in mind that they are of real people, and you never know if someone has a person close them that has this. Thank You, Sydney, Monica and Greer What Chromosome? •Albinism is a genetic order, which is caused by a gene on the ninth X (female) chromosome. Alleles • Alleles – an alternative form of a gene, which is located on a specific part of a certain chromosome. • 2 alleles per human gene. Recessive (aa): -trait will only appear if a dominant allele is not present. -homozygous Dominant (AA, Aa): -overpowers the recessive allele. -heterozygous Summary Of Albinism • Albinism – a rare, inherited, disease that you are born with, causing a lack in pigment or melanin. Usually, the person’s hair, eyes, and skin are affected. • Symptoms – Extremely light colored skin light/white colored hair pale blue/grey eye color, sometimes even pink very high risk of sunburn and skin cancer vision problems *Interesting Facts* There is no cure for Albinism, but precautions can be taken to alleviate the symptoms. - Staying out of the sun - contacts or seeing an optician Mode Of Inheritance •Albinism is recessive. • A male would have to inherit one affected X chromosome and females would have to inherit two affected X chromosomes to have the disorder. • It is not dominant because you do not get it every time, if one parent is a carrier. Both parents must contain the gene, whether they have the disease or not. • It is autosomal because you need two copies of the affected gene must be present in order for albinism to occur. Punnett Squares a A a Aa a A – dominant (normal gene) a – recessive (affected albinism gene) A Aa A aa aa a A aa Aa A Aa Aa a a A Aa Aa Aa Aa Probabilty • Ratios 1 : 2 : 1 1aa : 2Aa : 1AA a A A Aa AA a aa Aa • Percentages 25% : 50% : 25% 25% aa : 50% Aa : 25%AA Genotype and Phenotype a Probability A A Aa AA a aa Aa • Phenotype -Ratios – 3 brown hair : 1 white hair -Percentages - 75% brown hair : 25% white hair • Genotype - Ratios – 1AA : 2Aa : 1aa - Percentages – 25%AA : 2Aa :aa Key White – Healthy unaffected person. May carry one albinism gene. Orange – Affected with albinism, has two of the damaged genes Hypothetical Pedigree Andrew Ashley Laura Jonathon Leah George Nick Mary Max Claire Kim Meaning of the Albinism Punnett Square • AA – means that both genes are normal and they dominate. Aa – means that one gene is normal and one is affected with albinism. But since there is a normal gene that is dominant, it overpowers and the person is unaffected. aa – means that both genes are affected and the person has albinism • Phenotype (what is SEEN) if AA then normal brown hair is present if Aa then normal brown hair is present but the person is a carrier of the white hair gene if aa then the person has white hair. • Genotype (what is in the GENES) AA – Homozygous Dominant Aa – Heterozygous Dominant aa – Homozygous Recessive Student Practice a a a A Genotype: Ratio – Percentages – Phenotype: Ratio – Percentages – Hypothetical Pedigree (Student Practice) Key: •Pick 2 colors. •One for non effected •One for affected •Choose a Female and a Male •Who is married to who •The children they have •And probability of them being affected. The Rest is up to you! Pedigree Question and Answer: 1. How many affected parents are needed to produce a child with albinism? 2. What are the chances that the third generation of children will get albinism if only one child in the second generation was affected? 3. If both parents carry the gene what’s the chance that the child will not get albinism?