* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - Inducible Genes
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
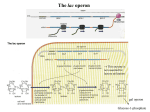
Genetic Regulatory Mechanisms Inducible Genes - Operon Model • Definition: Genes whose expression is turned on by the presence of some substance – Lactose induces expression of the lac genes • Catabolic pathways Lactose Operon Absence of lactose • Inducer -- lactose – Absence i p y a No lac mRNA – Presence • Negative control z Active • Active repressor • No expression • Inactivation of repressor • Expression o Presence of lactose i p o z y a Inactive -GalactosidasePermease Transacetylase Positive Gene Regulation- CAP – In E. coli, when glucose is always the preferred food source – When glucose is scarce, the lac operon is activated by the binding of the catabolite activator protein (CAP) Promoter DNA lacl lacZ CAP-binding site cAMP Inactive CAP Figure 18.23a RNA Operator polymerase can bind Active and transcribe CAP Inactive lac repressor (a) Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level high): abundant lac mRNA synthesized. If glucose is scarce, the high level of cAMP activates CAP, and the lac operon produces large amounts of mRNA for the lactose pathway. • When glucose is abundant, – CAP detaches from the lac operon, which prevents RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter Promoter DNA lacl lacZ CAP-binding site Operator RNA polymerase can’t bind Inactive CAP Inactive lac repressor (b) Lactose present, glucose present (cAMP level low): little lac mRNA synthesized. When glucose is present, cAMP is scarce, and CAP is unable to stimulate transcription. Figure 18.23b Induction of Lac Operon Transacetylase Lac repressor b-galactosidase 1. When lactose becomes available, a small amount of it is taken up and converted to allolactose by β-galactosidase. The allolactose binds to the repressor, causing it to fall off the operator site. Lactose Lac repressor Lactose permease 2. lac operon proteins are synthesized. This promotes the efficient metabolism of lactose. 4. Most proteins involved with lactose utilization are degraded. Lac repressor 3. The lactose is depleted. Allolactose levels decrease. Allolactose is released from the repressor, allowing it to bind to the operator site.