* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download jack of diamonds represents the gene for purple pigmentation
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
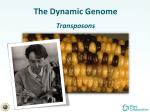
Agents that cause mutations are known as mutagens. •Radiation •Viruses •Transposons •Mutagenic chemicals Chemical mutagens include aflatoxin (from mold), caffeine (found in coffee and colas), LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide; a hallucinogenic drug), benzo(a)pyrene (found in cigarette and coal smoke), Captan (a fungicide), nitrous oxide (laughing gas), and ozone (a major pollutant when in the lower atmosphere). •Errors may also occur during meiosis or DNA replication. They can also be induced by the organism itself, by cellular processes such as hypermutation. Base-pair substitution: One base is wrongly paired with another (adenine to cytosine) during replication. Possible outcome is a different amino acid may replace another during protein synthesis, changing the resulting protein. People with sickle-cell anemia have this occur Mom fed the dog for Tad who was out all day Mop fed the dog for Tad who was out all day Insertions/Deletions: (Frameshift Mutation) One extra base is inserted, or deleted into a gene region. Remember this insertion or deletion can completely change the three-base codon/anticodon sentence. Mom fed the dog for Tad who was out all day. Mof edt hed ogf orT adw how aso uta lld ay? Transposons/Transpositions: When one or multiple bases jump around within the genome, moving spontaneously from one location to another in the same DNA molecule (or even to a different one) Mom out the dog for Tad who was fed all day. Sometimes called “Jumping Genes” Transposons are genes that move from one location to another on a chromosome. If the transposon moves to a position adjacent to a pigment-producing gene, the cells are unable to produce the purple pigment. This results in white streaks or mottling rather than a solid purple grain. The duration of a transposon in this "turned off" position affects the degree of mottling. If the pigmentation gene is turned off long enough by a transposon, the grain will be completely unpigmented. The reddish streaks on these corn grains are caused by transposons. Grains of Indian corn come in different colors, such as purple, yellow and white. Sometimes the kernels are streaked, or mottled. The movement of transposons on chromosomes may result in colored, non-colored and variegated grains The explanation for this phenomenon involves "jumping genes" or transposons, and earned Dr. Barbara McClintock the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1983 for her life-long research on corn genetics. The different cards represent a linear sequence of genes on a chromosome. The ace of spades represents a transposon that moves to different positions on the chromosome. The jack of diamonds represents the gene for purple pigmentation in the corn grain. When the transposon (ace of spades) moves to a position adjacent to the gene for pigmentation (jack of diamonds), the pigmentation gene is blocked and no purple is synthesized (white area). When the transposon moves away from the gene for pigmentation, pigment can again be coded for. Transposons may also have a profound effect on embryonic development and tumor formation in animal cells. • Oncogenes (genes that cause tumors) may be activated by the random reshuffling of transposons to a position adjacent to the oncogene. • Transposons may also be useful in genetic engineering with eukaryotic cells, by splicing in transposons to activate certain genes. • The implications from Barbara McClintock's discovery of transposons may be far-reaching and as significant as Watson and Crick's discovery of the structure of DNA. http://waynesword.palomar.edu/transpos.htm