* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Replication - Texas Tech University
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
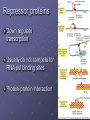
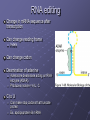
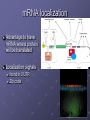
Transcriptional Control AHMP 5406 Lac Operon Bacterial example of a genetic switch Operon = group of genes transcribed from a single promoter Lac Operon Lac operon controlled by Lac repressor protein CAP Lac operon controls expression of lacZ gene Transcription allows bacterium to use lactose Regulation of Transcription in Euks. Promoters can be affected by regulatory proteins bound 1000’s of bp’s away Require several transcription factors Chromatin packaging can help regulation of transcription Gene control regions Control expression of genes Spread over long stretches of DNA Promoter Regulatory sequences Where regulatory proteins attach Gene activator proteins Have 2 domains One recognizes regulatory sequences Activation domain – increases rate of transcription initiation Influence position of RNA polymerase II holoenzyme Partially assembled Finished at the promoter Chromatin remodeling Can be directed by activator proteins Recruit remodeling proteins HATs (histone acetyl transferases) Histone acetylation increases accessibility Chromatin remodeling complex Transcriptional Synergy Many activators have a greater effect than a single activator Repressor proteins Down regulate transcription Usually do not compete for RNA pol binding sites Protein-protein interaction Co-activators/repressors Do not bind directly onto DNA Usually too weak to act on their own Bind to other regulatory proteins Post Transcriptional Controls Occur after RNA pol is bound to promoter Later in pathway Not as common as previous transcriptional controls Transcription attenuation Premature termination of transcription In bacteria transcript inherently forms 3D structure Interferes with transcription process What if the protein is needed? Regulatory proteins bind to nascent transcript Stabilize RNA to allow mRNA maturation Alternative Splicing RNA can be spliced in several ways Can make many different proteins from one transcript Can be tissue specific Drosophila example 38K genes from one transcript RNA editing Change in mRNA sequence after transcription Can change reading frame Indels Can change codon Deamination of adenine Adenosine deaminase acting on RNA enzyme (ADAR) Produces inosine = A,U, C C to U Can make stop codons that truncate protein Ex. apolipoprotein-B mRNA mRNA localization Advantage to have mRNA where protein will be translated Localization signals found in 3’UTR Zip code