* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 13.1: BIOTECHNOLOGY
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
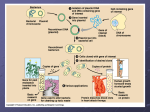
Ch. 13.1: BIOTECHNOLOGY Objectives: 1. Explain how the use of bacteria has contributed to the development of DNA technology. 2. List some recent research trends in recombinant DNA technology. Vocab: Biotechnology Recombinant DNA technology Biotechnology = Use of organisms to perform practical tasks. Examples: Use bacteria to make proteins/drug therapies Engineer plants with natural resistance to insects, drought, fungi, etc. Develop vaccines. Recombinant DNA = DNA from 2 different sources combined. 13.2: Bioengineering Objectives: 1. Explain the role of plasmids in 2. 3. 4. engineering bacteria. Explain how biologist “cut and paste” DNA. Describe the procedure used in cloning a specific gene. Identify the usefulness of recombinant microorganisms. Vocab: Plasmid Genomic library Restriction enzyme Nucleic acid probe Bacteria: Work horses of Biotech. Used to mass produce useful genes + proteins. Simple organisms 1 chromosome. Plasmids Reproduce rapidly Easy to manage in a lab. Bacteria Plasmids Small, circular DNA Separate from chromosome. Contains a few genes. Make copies of itself Can be shared/ transferred b/w bacteria. Exchange of plasmids is how bacteria build genetic variation. Genes for antibiotic resistance are shared this way :( Making Recombinant DNA 1. Remove desired gene from donor cell. 2. Remove bacteria plasmid. 3. Insert gene into plasmid. 4. Return plasmid to bacteria. 5. Gene is transcribed and translated into protein product. Recombinant DNA http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/0072437316/120078/bio38.swf::Early Restriction Enzymes = Enzymes that CUT foreign DNA sequences. Each enzyme is cuts a specific sequence (CCCGGG or GAGCT) Cuts sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA Make staggered cuts. Leave “sticky ends” on cuts. Evolved in bacteria to protect bacteria fr. invading viruses. Restriction Enzymes: Cut DNA into fragments BLUNT ends =no staggered cuts; not as useful Sticky ends = made by staggered cuts; unpaired bases; useful b/c they h-bond w/ complimentary bases in other fragments. Helps to “sew” fragments together & make recomb. DNA. Ligase: Glues DNA fragments together Genetic Cloning = Copies of recomb. DNA (and resulting proteins) are made by reproducing organisms Genomic Library = Complete collection of cloned DNA fragments from an organisms. When you use restriction enzymes they cut up the donor DNA into MANY fragments. Each fragment is incorporataed into a plasmid. You need to figure out which bacteria has desired recomb. Plasmid! Identifying Desired Recomb. DNA 1. Use nucleic acid probe Radioactively labeled complimentary sequence (TAGGCT will find and bind to ATCCGA when strands are separated). 2. Insert desired DNA into plasmid sequence for antibiotic resistance. Recomb. plasmids will lose resistance to antibiotics and will NOT survive when exposed to antibiotic. Task: Diagram Steps in Creating recombinant DNA clones Use and illustrate the following key terms… Host DNA Bacteria Plasmid Vector Restriction Enzyme Sticky Ends Ligase Bacteria reproduces/plasmid replication Recombinant DNA Clones Lab: Recombinant Paper Plasmids Goal: Insert human gene for insulin production into bacteria plasmid. 1. Construct bacteria plasmid. Color code sequences for antibiotic resistance. 2. Label 3’ and 5’ ends of restriction enzymes and plasmid DNA. 3. Identify restriction enzymes that will cut plasmid in sequence for antibiotic resistance. Mark these locations and label the enzyme used. Lab: Recombinant Paper Plasmids Goal: Insert human gene for insulin production into bacteria plasmid. • Label 3’ and 5’ of human DNA • Determine the enzyme that will allow for removal of human insulin gene AND match up with the sticky ends on the plasmid. • Create the recombinant plasmid.