* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Schuette Science
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
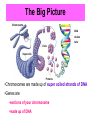
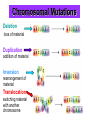
MUTATIONS Mistakes in DNA The Big Picture Chromosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Proteins •Chromosomes are made up of super coiled strands of DNA •Genes are •sections of your chromosome •made up of DNA Mutations • • Mutations are changes in genetic material. There are two major mistakes that can happen: 1. Chromosomal Mutations 2. Gene Mutations Type 1: Chromosomal Mutations • Whole chromosome is affected. • Large sections of DNA can be – – – – Removed from a chromosome Added to a chromosome Rearranged within a chromosome Switched with DNA from another chromosome. • These mutations are usually very harmful Chromosomal Mutations Deletion loss of material Duplication addition of material Inversion rearrangement of material Translocation switching material with another chromosome Type 2: Gene Mutations • Changes that occur in a single gene. • Change occurs at the DNA nucleotide level Nucleotide Hydrogen bonds Sugarphosphate backbone Key Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Two Types of Gene Mutations 1. Point mutations: one nucleotide that affects one amino acid. Example: Substitution C changes to G Two Types of Gene Mutations 2. Frameshift mutations: • • involve the reading of the DNA or m-RNA strand many amino acids are affected. Examples: Insertion Deletion Mutation Can Be… 1. Neutral (a.k.a. Silent) • Example: Substitution • UCU = Serine if the last U is changed to C, A or G the mRNA will still make Serine 2. Harmful • Example: Substitution • Sickle Cell Anemia • There is a change 17th nucleotide in the code for hemoglobin • A is changed to a T - GAG changes to GTG • How does this change the amino acid? • GLU changes to VAL • This changes hemoglobin’s shape from round to sickle shaped Mutation Can Be… 3. Harmful (more harmful) • Example: Frameshift - Deletion • Shifts the whole reading frame • Changes the amino acids produced 4. Harmful (even more harmful!) • Example: Chronic myelogenous leukemia • Translocation • Pieces of 2 chromosomes switch • Causes white blood cells to divide and reproduce improperly.