* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stages and mechanisms of translation, regulation of translat
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
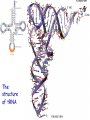
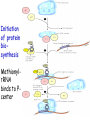
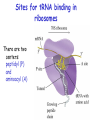
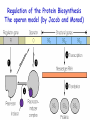
Stages and mechanisms of translation, regulation of translation. Antibiotics – ingibitors of transcription and translation STAGES OF TRANSLATION • 1. Recognition • 2. Initiation • 3. Elongation • 4. Termination RECOGNITION O R1 CH COOH + H O O P O P OH NH2 O O OH P O Аденозин OH O R1 CH CO O P O Аденозин + H4P2O7 OH NH2 Aminoacyladenilate Aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase Aminoacyladenilate + tRNA aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP Activation of amino acids Each amino acid has a specific tRNA There is specific aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase for each AA The structure of tRNA Initiation of Translation • The translation complex is assembled at the beginning of the mRNA coding sequence • Complex consists of: -Ribosomal subunits -mRNA template to be translated -Initiator tRNA molecule -Protein initiation factors Initiator tRNA • First codon translated is usually AUG • The initiator tRNA recognizes initiation codons -Bacteria: N-formylmethionyl-tRNA -Eukaryotes: methionyl-tRNA Initiation of protein biosynthesis MethionylтRNA binds to Pcenter Sites for tRNA binding in ribosomes There are two centers: peptidyl (P) and aminoacyl (А) Elongation 1) Positioning of the next aminoacyl-tRNA in the A site 2) Formation of the peptide bound (enzyme – peptidyl transferase) between methionine and AA in Acentre. The residue of methionine is transferred on the amino group of another AA 3) Translocation – shift of ribosome by one codon. Methionyl-tRNA is released from P-centre. DipeptidyltRNA moves from A-centre to P-centre. Termination of Translation • Ribosome comes to terminal codon UGA, UAG or UAA • No tRNA molecules recognize these codons and protein synthesis stalls • Protein termination factors F-1, RF-2, RF-3 split off synthesized polypeptide from the last tRNA • Ribosomal complex dissociates Termination of Translation POSTTRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATION 1) Preparing of proteins for different functions 2) Direction of proteins to different locations (targeting) 1. Removing of methionine (formylmethionine) 2. Formation of disulfide and other bonds (secondary, tertiary structures) 3. Proteolytic cleavage 4. Modification of amino acid residues: - Hydroxylation - Glycosilation - Phosphorilation 5. Joining of prosthetic groups or cofactors 6. Formation of the quaternary structure Regulation of the Protein Biosynthesis The operon model (by Jacob and Monod) Inhibitors of Transcription Antibiotics inhibiting protein synthesis