* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nucleic acids - onlinebiosurgery
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
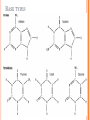
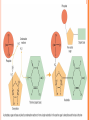
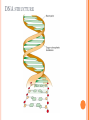
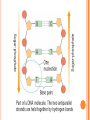
NUCLEIC ACIDS Objective: describe the structure of RNA and DNA and explain the importance of base pairing and hydrogen bonding - DNA is a polynucleotide, usually double stranded, made up of nucleotides with bases A,T,C and G. - RNA is a polynucleotide, usually single stranded made up of nucleotides containing the bases A,U,C and G. CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY •DNA •RNA •Protein HOMEWORK: Devise and complete a table of key roles for each specified ion – information coming from bibliographic and web-based research in living organisms: calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride, nitrate, phosphate NUCLEIC ACIDS 1) 2) They come in two forms: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (Ribonucleic acid) DNA in eukaryotic cells are found in the nucleus, acting as a information store. CONTINUED… Nucleic acids are composed of monomers called a nucleotide. A nucleotide is composed of 3 subunits: One phosphate group; One sugar molecule ; One organic nitrogenous base. These subunits are joined by covalent bonds to form a nucleotide molecule. BASE TYPES FEATURES OF NUCLEOTIDES DNA(double helix) RNA(single) Same phosphate group Same phosphate group 5-carbon sugar normally deoxyribose 5-carbon sugar normally ribose Base pairs Guanine, Cytosine, Adenine and Thymine Base pairs, Guanine, Adenine, Cytosine and Uracil. JOINING NUCLEOTIDES A condensation reaction between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another join the two together. This forms chains called the “Backbone.” Organic bases will project from this, and it is this sequence of bases that forms coded information of nucleic acid. HOW NUCLEOTIDES JOIN TOGETHER DNA STRUCTURE BASE PAIR- ACRONYM Gangsters – Can Ask - Time A-T 2 H bonds G-C 3 H-bonds DRAW AND LABEL THE DIAGRAM EVERY COMPONENT AND BOND DRAW AND LABEL ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Makes up the bulk of the ribosome. Large folded molecule. messenger RNA (mRNA) Carries the genetic message from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesised (made) accordingly. Long molecule, not folded. Variable in length and base sequence. Readily broken down and remade. transfer RNA (tRNA) Collects amino acids and takes them to the ribosomes for assembly into proteins. AMINO ACID Small molecule. Winds back on itself to form a “clover-leaf” shape. One end carries an amino acid. One loop has a special triplet of bases (ANTICODON) which determines the amino acid carried. ANTICODON RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA) Single stranded polynucleotide. Sugar is always ribose. Organic bases are always A, G, C, and U, NEVER T. 3 types :- ribosomal RNA (rRNA) messenger RNA (mRNA) transfer RNA (tRNA) Back