* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
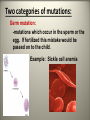
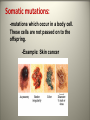
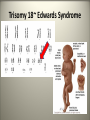
Mutations What are mutations? -They are mistakes made in our genetic code, which may or maynot result in the wrong protein being made. Mutagens: Are any chemical or radiation that causes a change in our genetic code. Examples: X-rays, UV sunrays, asbestos and coal dust. Carcinogens: -Are mutagens that cause a mistake in the genetic code that leads to uncontrollable cell division. - This results in CANCER. -Examples include: Mercury, UV rays and cigarettes Two categories of mutations: Germ mutation: -mutations which occur in the sperm or the egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia Somatic mutations: -mutations which occur in a body cell. These cells are not passed on to the offspring. -Example: Skin cancer Types of mutations (either germ or somatic): 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. -Example: Down Syndrome Edwards Syndrome Trisomy 21~Down Syndrome Trisomy 18~ Edwards Syndrome 2. Gene mutation: -One single change in a DNA nucleotide is made therefore only affecting one single gene. Example: Albinism: Types of gene mutations: 1. Silent or Neutral Mutation -a change in one base does not alter the amino acid sequence. 2. Missense Mutation: -one DNA nucleotide is changed causing it to code for a different amino acid. This mistake still codes for an amino acid BUT just the wrong amino acid. 3. Nonsense Mutations: -one DNA nucleotide is changed forming a stop codon in the middle of a gene resulting in a shortened amino acid sequence that codes for NO protein. 4. Frameshift mutation: -one or two nucleotides gets added to a gene resulting in the entire sequence to get shifted down and throwing off the entire amino acid sequence.