* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IOBC Hasselt
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
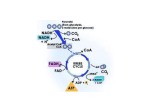
Implication of the pentoses phosphates pathway in the antagonist effect of P.anomala. Anthony Kwasiborski1, Jenny Renaut2, Pierre Delaplace3, Philippe Lepoivre1 & Haïssam M. Jijakli1 1 Plant Pathology Unit, GxABT, Ulg, Gembloux Proteomic plateform, CRPGL, Luxembourg 3 Plant Biology Unit, GxABT, Ulg, Gembloux 2 Objective Background 5-20% loss Material and methods - B. cinerea P. expansum Gloeosporium spp. Results Chemical fungicide Resistant Fungal Biological control - P. anomala Kh6 90% of protection B. cinerea cDNA-AFLP: 11 transcripts of P. anomala overexpressed in presence of B. cinerea cell walls GENE DISRUPTION: Implication of PAEXG1 et PAEXG2 in the mechanism of action of P. anomala MUTANTS paexg1 and/or paexg2: Decrease of protective level to 8% Restoration of the protective level: - ! - Yeast inoculum concentration Maturation of apples Complexicity of the mechanism of action Study of mode of action, without a priori, at the ultime expression level of the genome Mechanism of action Apples production Background Objective Material and methods Results Conditions closed to the natural infection: Tripartite interaction: HOST / ANTAGONIST / PATHOGEN Mechanisms of action: P. anomala vs. B. cinerea Proteomic tool: Global view without a priori of the metabolic actors: PROTEINS Background Objective Material and methods Results Interaction Model YEAST INOCULATION Wash and Overnight dry P. anomala 400µL / 107 ufc/mL B. cinerea 400µL / 106 sp/mL OR mock inoculation 7h of incubation Exponential phase After 1h Membrane 47mm / 0.45µm 24h of incubation Stationary phase YEAST RECOVERY Membrane in isotonic water vortex 20s Wash with ultra pure water Store at -20°C Objective Background Material and methods Interaction Model Proteins study Protein extraction Hot SDS buffer Mechanical Lysis (Homogenization of 2.5min) Thermal Lysis (70°C for 3min + 15min on ice) Acetone precipitation 2D-electrophoresis 1st dimension: 100µg of proteins 24cm / pH 4-7 IPG strips 2nd dimension: SDS-PAGE 12.5% Proteins identification Gel analysis: Decyder v 7.0 Identification: MALDI-ToF Proteins influenced by the presence of B. cinerea Results Background Proteins synthesis Energetic metabolism EXPONENTIAL PHASE Objective Material and methods Results K1 vs. KB1 S-Co-S PDH Protein function ATPase Glycolysis Cyt Bc1 Citric acid cycle Cyt c Oxidative phosphorylation Pentose phosphate pathway Nucleotide synthesis Transcription Amino acid synthesis Ribosome synthesis Translation Cell division 6-PGD TK K1 KB1 3 2 1 0 1 0 4 2 7 5 2 2 5 3 4 0 5 1 7 3 Exponential phase K1= P. anomala alone KB1= P.anomala + B.cinerea F-1,6-BP TPI Use of Glycolysis pathway Energetic metabolism orientated to Oxidative phosphorylation New orientation of the genomic expression Cytoplasm Pentose Phosphate Pathway Glucose NADPH,H+ Nucleic acids G6P Ru5P Nucleic acids F6P Xu5P DHAP R5P ATP Oxidative phosphorylation GA3P ATP Citric acid cycle Glycolysis Pyruvate Mitochondria Background Objective Material and methods Results K1 vs. KB1 Stationary phase K2 vs. KB2 K2= P. anomala alone KB2= P.anomala + B.cinerea STATIONARY PHASE Protein Energetic synthesis metabolism Protein function K2 KB2 Glycolysis 3 5 Alcoholic fermentation 3 2 Nucleotide synthesis Amino acid synthesis Ribosome synthesis Traduction 0 0 0 0 1 3 1 1 Energetic metabolism orientated to Alcoholic fermentation Metabolic delay of P. anomala in presence of B. cinerea Conclusion Exponential phase In presence of B. cinerea Orientation of energetic metabolism from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation of P. anomala Set up the pentose phosphate pathway to answer to its needs EFFECTIVE COLONIZATION OF THE SUBSTRACT Stationary phase In absence and presence of B. cinerea Orientation of energetic metabolism to alcoholic fermentation of P. anomala In presence of B. cinerea Metabolic delay due to the presence of B. cinerea