* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL METABOLISM - My Anatomy Mentor
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
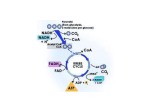
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Equation for CHO metabolism: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6 H20 + 6CO2 + 36 (38)ATP + heat Accomplished by: – glycolysis – Krebs cycle – electron transport system GLYCOLYSIS Series of reversible reactions Occurs in the cytoplasm Anaerobic Overview: glucose 2 pyruvic acid 2 net ATP formed (4 total made; 2 used = 2 net) KREBS CYCLE A cyclic series of reactions Occurs in mitochondria Oxidative & substrate phosphorylation Oxygen is used in the associated electron transport system. Most ATP formed here by oxidative phosphorylation KREBS CYCLE Products: NADH, FADH2, ATP By-products of Krebs cycle: CO2 metabolic water ELECTRON TRANSPORT SYSTEM On cristae of mitochondria Aerobic - referred to as OP Captured electrons brought here by carriers (NADH, FADH ) 34 ATP 2 Other Processes of Metabolism Glycogenesis Formation of glycogen from glucose Stored in: liver & muscle Glycogenolysis Conversion of glycogen to glucose Gluconeogenesis Formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources Summary of Metabolism Glucose Proteins Lipid Krebs cycle 36-38 ATP Most by oxidative phosphorylation at ETS SMOOTH MUSCLE - 1 Appearance •small; •spindle shaped; •uninucleate; •no striations; •in sheets; •no connective tissue coverings SMOOTH MUSCLE - 2 • Cell Structure poorly developed SR T-system absent - caveolae actin & myosin present; no sarcomeres tropomyosin present troponin absent SMOOTH MUSCLE - 3 • Contraction electrical coupling - gap junctions pacemaker cells ATP calcium important - calmodulin prolonged - low energy cost - fatigue resistant multiple stimuli