* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.4 Transcription - Issaquah Connect
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
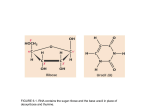
8.4 Transcription KEY CONCEPT Transcription converts a gene into a single-stranded RNA molecule. 8.4 Transcription The transcription process is similar to replication. • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a gene. – Replication makes one copy; DNA transcription can make many copies. 8.4 Transcription • The central dogma states that information flows in one direction from DNA to RNA to proteins. • The central dogma includes three processes. – Replication – Transcription – Translation • RNA carries DNA’s instructions to make proteins replication transcription translation 8.4 Transcription • RNA differs from DNA in three major ways. – RNA has a ribose sugar. -DNA uses deoxyribose – RNA has uracil instead of thymine. -DNA uses Thymine – RNA is a single-stranded structure.-DNA is double stranded 8.4 Transcription • Transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase. 1. The transcription complex (made of RNA polymerase and other proteins) recognizes the start site of a gene and begins to unwind the DNA. start site 7. transcription complex 5. nucleotides 8.4 Transcription 2. a. RNA polymerase reads one side of the DNA template b. It strings together a complementary strand of RNA nucleotides. c. The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed. d. RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. 4. Original DNA Strand DNA RNA polymerase moves along the DNA 6. New RNA Strand 8.4 Transcription 3. The growing RNA strand hangs freely as it is transcribed and detaches from the DNA once the entire gene is transcribed. RNA 8.4 Transcription • Transcription makes three types of RNA. – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms the part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids (protein “parts”) from the cytoplasm to a ribosome to help make a growing protein.