* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription - Santa Susana High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
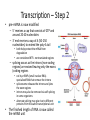
Transcription • Vocabulary of transcription: • transcription - synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA • messenger RNA (mRNA) - carries genetic message from DNA to the ribosome for the synthesis of protein • translation - synthesis of protein under the direction of mRNA • ribosome - site of protein synthesis (translation) • primary transcript - RNA that comes directly from the transcription of DNA • codon - a triplet code of DNA (64 possible) that codes for an amino acid • reading frame - indicates the proper starting & ending points for the transcription of DNA • amino acid (AA) - building block of proteins based on a 3-letter code of DNA Genetic Code • 64 codons for 20 amino acids – Called a redundant code as different codons create the same amino acid • AUG start … Methionine • UAA, UAG, & UGA Stop – Each amino acid abbreviated by the 1st 3 letters of the name Transcription – Step 1 • RNA polymerase II pries apart DNA – reads the DNA in the 3'-5' direction (sense strand) beginning at the start codon AUG • binds to the DNA prior to the start codon in the promoter region – TATA Box 5'-TATAAAA-3" (full sequence about a dozen nucleotides long) – used for the attachment of transcription factors that aid in the binding of RNA pol II » transcription factors + RNA pol II is called the transcription unit – assembles RNA in the 5'-3' direction • can be assembled by multiple RNA pol II enzymes – transcription continues until a stop codon (terminator) is reached • stop codons are UAA, UAG, UGA • the pre-mRNA also continues a poly-A tail (AAUAAA) before it is cut free from the growing strand • RNA pol II falls off of the DNA Transcription – Step 2 • pre-mRNA is now modified – 5' receives a cap that consists of GTP and around 20-40 nucleotides – 3' end receives a cap of A (50-250 nucleotides) to extend the poly-A tail • both help protect the mRNA from degradation • are considered NTR - nontranslated regions – splicing occurs as the introns (non-coding regions) are excised leaving only the exons (coding regions • cut by snRNPs (small nuclear RNA) specialized RNA that remove the introns • spliceosome releases the introns and joins the exon regions • introns may also be removed via self splicing in some organisms • alternate splicing may give rise to different proteins from the same transcriptional unit • The finished length of RNA is now called the mRNA unit