* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GeneChip Hybridization
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
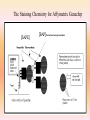
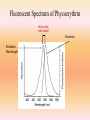
GeneChip Hybridization The following hybridization mix is prepared for each sample Fragmented cRNA 5ug Control B2 Oligo 20x Eukaryotic Control mix [bio B, bio C, bio D, Cre] Herring Sperm DNA [10mg/ml] Acetyleted BSA [50mg/ml] DMSO 2x Hybridization Buffer Water 10 ul 1.7 ul 5 ul 1 ul 1 ul 10 ul 50 ul 22.3 ul Denature 99C Inject into 10 minutes GeneChip The hybridization oven Target binds to the Probes RNA-DNA Hybridization Targets: Antisense biotinylated cRNA Probe sets: The DNA oligo probe is attached to the GeneChip via a silane bond Hybridization Optimized Hybridization is the process of single stranded nucleic acids binding to another strand with identically complement sequence [We hope] Types: DNA to DNA DNA to RNA RNA to RNA PNA to DNA Stringency Stringency is a condition that causes a change in the local hybridization environment and “interferes” with the binding kinetics Stringency prevents: . Binding of non-complementary strands Self hybridization – hairpin formation Disassociation of strands Factors Influencing Stringency Intrinsic factors GC rich nucleic acid more stable because of triple H-bond Degree of complementarity Extrinsic factors Experimentally introduced Temperature Salt concentration- NaCl, Na citrate, morpholinoethanesulfonic acid Presence of denaturing agents (e.g., formamide) Presence of high molecular weight polymers (e.g., dextran sulfate) Shear forces Molecular tagging Stringency In Microarray Hybridization High stringency is obtained by: Low salt or buffer concentration High temperature Low stringency is obtained by: Lowering the temperature of hybridization Increasing salt concentration [to a point] This is different then PCR, because increasing salt concentration increases stringency This is because of the enzyme activity of taq polymerase and Molecular interference High Stringency vs. Low Stringency The fluidics station Staining the biotinylated cRNA An automated system to stain the target using streptavidin-phycoerythrin [SAPE], a biotinylated anti-SAPE antibody, and SAPE again… high and low stringency buffers are used Steps in the Staining Protocol Rinse away unhybridized FcRNA target Stain with Streptavidin PE [SAPE] Stain with Biotinylated IgG anti-SAPE antibody Grand Total MW (Minimum) Stain AGAIN with Streptavidin PE [SAPE] 292,800 150,244 Rinse throughly 292,800 735,844 Da WOW!!! The Staining Chemistry for Affymetrix Genechip Scanning the Yeast 2.0 GeneChip with the GS3000 -Nd-YAG laser 532nm -2.5 uM resolution Fluorescent Spectrum of Phycoerythrin What is this shift called? Emission Excitation Wavelength The Scanned Yeast Array 220,000 probes 6,400 genes 11 um features 25 bp Sense DNA Oligo’s