* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis - OpotikiCollegeBiology
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
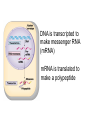
Protein Synthesis Making proteins – one of the jobs of genes. Ribosomes • Cell organelle that is the site of protein synthesis. • In the cytoplasm • Linked by endoplasmic reticulum • to vesicles that release/secrete the protein the ribosome made. Two problems – location and structure • The code for the protein is in the chromosomes. • The chromosomes are in the nucleus. • How does the info get from the chromosomes in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm? Two problems location and structure • The code is written in nucleotide bases and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? • Each group of 3 nucleotide bases in the DNA is called a triplet. • The triplet can’t leave the nucleus, so another nucleic acid comes to the nucleus to read it. Transcription (using the same code) • This messenger is called mRNA. • The three bases that match the DNA triplet are called a codon. • E.g DNA • mRNA TGC GGA CCG GAG ACG CCU GGC CUC • Manual pg 85. Translation (changing to a new code) • At the ribosome• The codon comes in and brings the code. • The tRNA reads the codon and goes off to get the right Amino Acid. • The Amino Acids are linked together inside the ribosome to form the protein. • Manual pg 86, 87. DNA is transcripted to make messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA is translated to make a polypeptide • How does the mRNA know when to start and when to stop reading? • Special codons that tell them • Manual pg 71. The genetic code. Polypeptides and proteins • A long chain of amino acids is called a polypeptide (many peptide bonds!). • Sometimes a protein is made of several polypeptides joined together. This will require information from the same number of genes. • One chromosome has many genes in the exon sections. • Each gene codes for one polypeptide chain. • The group of genes that code for the protein are called a transcription unit. • Michael pg 84 introns and exons. Whole picture Manual pg 78. Protein synthesis and Replication together Manual pg 79.