* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular Genetics
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
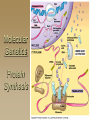
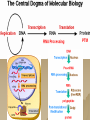
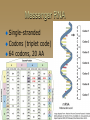
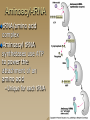
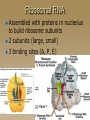
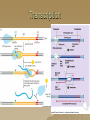
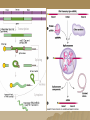
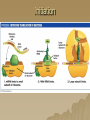
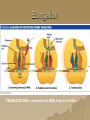
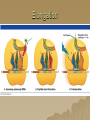
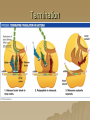
Molecular Genetics Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Traits are end products of metabolic processes regulated by enzymes (proteins) A gene is a DNA segment that encodes a particular polypeptide Gene expression is the process in which proteins are assembled from the information contained in DNA Messenger RNA Single-stranded Codons (triplet code) 64 codons, 20 AA Transfer RNA 3’ end carries amino acid Anticodon pairs with mRNA – 3rd nucleotide can “wobble” – Thus can pair with more than 1 codon – Only 45 tRNAs (bind to 61 AA codons) Aminoacyl-tRNA tRNA/amino acid complex Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases use ATP to power the attachment of an amino acid – Unique for each tRNA Ribosomal RNA Assembled with proteins in nucleolus to build ribosome subunits 2 subunits (large, small) 3 binding sites (A, P, E) Transcription Initiation – RNA poly binds to promoter site (TATA) – DNA unzipped by RNA poly Elongation – RNA poly unzips & assembles mRNA – Builds in 5’ → 3’ direction Termination – RNA poly reaches termination sequence (polyA) – Pre-mRNA & transcription factors released Transcription mRNA Processing Before mRNA leaves the nucleus: 1. Addition of 5’ Cap (-P-P-P-G-5’) GTP - For stability and ribosome attachment 2. Addition of 3’ Poly-A Tail (-A-A-A…A-A-3’) ~200 A’s - For stability and crossing the nuclear envelope 3. RNA Splicing of exons and introns - Exons “express”, Introns “intervening” - snRNP’s delete introns (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) - Alternative splicing allows different mRNA’s to be made from the same pre-mRNA transcript Translation 1. 2. 3. Initiation Elongation Termination Powered by GTP Initiation Elongation TRANSLOCATION = movement of tRNA from A to P site Elongation Termination Post-translational Modification Folding Lipid groups added for membrane localization Cofactors added for enhanced enzymatic function Glycosylation (sugar groups) Ubiquitin (destruction at proteasome)