* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins and Enzymes - Downtown Magnets High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
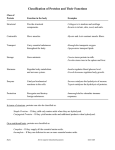
Macromolecules Part Two: Proteins Biology Standard 1 b Organic Group: Proteins • Compounds that contain N, C, H, and O. • Made of polymers of amino acids. Amino Acid Structure • 20 diff. amino acids exist • ‘R’ Side Chain differs on all of them Case Study: Hemoglobin • Iron-containing protein found in red blood cells. • Transports oxygen to body Peptides • Peptide bonds: join amino acids together. • Dehydration synthesis (forms proteins) Eat Your Proteins! Eat Your Polypeptides ! Enzymes • Proteins! • Speed up rates of reactions w/out being altered (changed). • Lower activation energies of reactions Lower activation energies of reactions How Do They Work? • Each enzyme: a very specific active site in which a substrate can bind. • When a substrate binds reaction occurs. • Enzyme remains unchanged in reaction. • Competitive inhibitors: interfere w/ process. Case Study: Lactase • Enzyme that helps break down sugar lactose into galactose and glucose. • Lactose intolerant: you don’t make lactase. Mutation of Chromosome 2. • Cramps, bloating, flatulence