* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz Next Tuesday (09/18) - Chemistry at Winthrop University
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
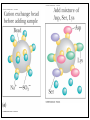
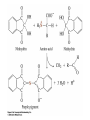
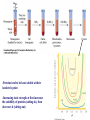
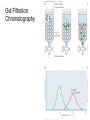
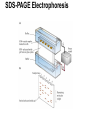
Quiz Next Tuesday (09/18) Figure 4.18 Cation (a) and anion (b) exchange resins commonly used for biochemical separations. Figure 4.21 Chromatographic fractionation of a synthetic mixture of amino acids on ion exchange columns using Amberlite IR-120, a sulfonated polystyrene resin similar to Dowex-50. A second column with different buffer conditions is used to resolve the basic amino acids. (Adapted from Moore, S., Spackman, D., and Stein, W., 1958. Chromatography of amino acids on sulfonated polystyrene resins. Analytical Chemistry 30:1185–1190.) 5.1 - What Is the Fundamental Structural Pattern in Proteins? Figure 5.3 The -COOH and - NH3+ groups of two amino acids can react with the resulting loss of a water molecule to form a covalent amide bond. The Coplanar Nature of the Peptide Bond Six atoms of the peptide group lie in a plane! Figure 5.4 Anatomy of an amino acid. Except for proline and its derivatives, all of the amino acids commonly found in proteins possess this type of structure. 5.2 – What Architectural Arrangements Characterize Protein Structure? • Proteins are classed according to shape and and solubility • Shape - globular or fibrous • The four levels of protein structure - Primary- Secondary - Tertiary – - Quaternary - Proteomics: Studying Protein Structure and Function -Proteins tend to be least soluble at their isoelectric point -Increasing ionic strength at first increases the solubility of proteins (salting-in), then decreases it (salting-out) Gel Filtration Chromatography Affinity Chromatography SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis