* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Did Life Begin? Unit Objectives Vocabulary: Miller
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
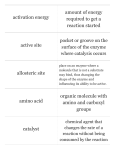
How Did Life Begin? Unit Objectives Vocabulary: Miller-Urey Experiment, Cell Theory, Organic Molecule, Inorganic Molecule, Amino Acids, Covalent Bonds, Peptide Bonds, Proteins, Dehydration Synthesis, Hydrolysis, Catalyst, Enzyme, Catalase Active Site, Substrate, Hydrogen Peroxide, Oxygen, Lock and Key, Induced Fit, Activation Energy, Reaction Rate, Stability, Reactivity, Denature, Acid, Base, pH By the end of this unit students will be able to: o Describe what it means to be alive using no less than six criteria. o List the two components of cell theory and explain how they apply to the fossil record explored in unit 1 and the origin of life itself. o Explain the origin of organic molecules from inorganic matter. o Describe the Miller-Urey experiment, what it tested, and what the results indicate. o Describe the relationship between monomers, polymers, proteins, and enzymes. o Explain the nature of covalent bonds and their relative strength in living systems. o Sketch the structure of an amino acid and explain how it can bond with a neighboring amino acid. o Explain what an enzyme is, how it causes stable molecules to react, and why they work well / poorly under varying conditions (temperature & pH). o Analyze and draw meaningful conclusions from graphs depicting enzyme activity in various conditions.