* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleotide Metabolism - Indiana University
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
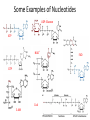
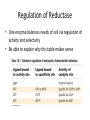
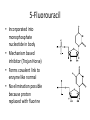
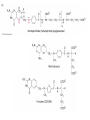
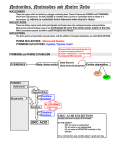
Nucleotide Metabolism C483 Spring 2013 1. A ribose sugar is added to ________ rings after their synthesis and to ________ rings during their synthesis. A) purine; pyrimidine B) pyrimidine; purine C) purine; purine D) pyrimidine; pyrimidine 2. The first nucleotide product in the de novo biosynthetic pathway of purines is A) AMP. B) GMP. C) IMP. D) XMP. 3. Which of the following statements is false concerning purine synthesis? A) N7 is from glycine B) C2 is from carbon dioxide (bicarbonate) C) N3 is from glutamine D) C8 is from 10-formylTHF. 4. Which is a precursor in the de novo synthesize CTP? A) CMP. B) GMP. C) TMP. D) UMP. 5. Which of the following is not a role of a catalytic sulfur atom in ribonucleotide reductase? A) Proton donor B) Radical stabilization C) Redox reaction D) Covalent catalysis 6. Dihydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthetase are major targets for anticancer drugs because A) these enzymes are unique in cancer cells. B) cancer cells lack sufficient amounts of these enzymes. C) cancer cells grow rapidly and are very dependent upon the activities of these enzymes. D) they donate one-carbon groups. E) All of the above. Terminology of Nucleic Acids • • • • • • • Nucleotide Nucleoside Nucleobase AMP ADP ATP dAMP Some Examples of Nucleotides UDP-Glucose ATP NAD+ GTP CoA S-AM FAD De Novo Synthesis De Novo Synthesis of Purines • Form activated ribose • Form 5-phospho ribosylamine • Build IMP from precursors • Synthesis of AMP and GMP PRPP • Pentose phosphate pathway • 2 ATP equivalents • Over production of PRPP is one cause of gout because PRPP stimulates the next step… 5-phosphoribosylamine • First step of purine biosynthesis • Glutamine is N donor • Regulated – Activation by PPRP – Increased purine levels – Degradation of purines leads to compound which can cause gout Purine Pathway • Don’t need to know details, order • Know precursors – N from Asp, Gln – C from THF, Gly, CO2 • Cost – 2 ATP eq for PRPP – 5 more ATP steps Know this figure! Purines • Two distinct strategies for amination – Mechanisms • Regulation – Feedback to 5-phospho ribosylamine – Branchpoint regulation Compare/Contrast • Purine biosynthesis – Salvage is a major pathway – Base synthesized while attached to ribose – IMP is common intermediate for AMP and GMP, but itself is not a typical nucleotide • Pyrimidine biosynthesis – De novo is a major pathway – Base is synthesized, then attached to ribose – UMP, a typical nucleic acid, is converted into other pyrimidines De novo Pyrimidine Synthesis • First step regulated (compare to urea cycle) • Asp is different than purine— whole molecule is incorporated Further Modifications • Interconversion of nucleotides (mono, di, tri phosphates) • Reduction to form deoxynucleotides • Methylation to form dTMP Nucleotide Interconversions • Fast, reversible, driven by high [ATP] • NMPNDP catalyzed by specific nucleoside monophosphate kinase • NDPNTP catalyzed by nonspecific kinase • AMP + ATP ADP + ADP important in energy balance Deoxyribonucleotides • Deoxygenation occurs on diphosphates • One enzyme affects all transformations [dUDP] Ribonucleotide Reductase • Sulfur does amazing chemistry! – Stable radical – Proton donor – Redox reagent • NADPH is ultimate source of reducing Regulation of Reductase • One enzyme balances needs of cell via regulation of activity and selectivity • Be able to explain why this table makes sense Methylation • • • • dTMP is made from dUMP Key step in replicating cells Therapeutic target for anti-cancer drugs Two key enzymes Thymidylate Synthase • Methylene-THF acts as a “methyl” donor – Donates methylene – And hydride • Fascinating chemistry! – Sulfur is covalent catalyst – Internal 1,3-hydride shift • THF is left as DHF 5-Fluorouracil • Incorporated into monophosphate nucleotide in body • Mechanism based inhibitor (Trojan Horse) • Forms covalent link to enzyme like normal • No elimination possible because proton replaced with fluorine DHF reductase • DHF must be reduced back to THF to be a viable cofactor • Second chemotherapy target • Competitive inhibitor that is structurally similar to THF would end methylation process Review of Purines • Knowing blue in figure will help with chapter summary Review of Pyrimidines • Knowing blue in figure will help with chapter summary Catabolism • Less important than other catabolic processes – not a major energy source – Lots of salvage – Serves to clear excess • In humans, purines uric acid (excreted) • In humans, pyrimidines acetyl CoA, succinyl CoA for some energy gain Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Syndrome (SCIDS) • Deficiency of adenosine deaminase • First step in catabolism • High levels of dATP lead to low levels of dNTP • No DNA kills fast growing T-cells * Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. B C B D D C