* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biosynthesis of Nucleotides Biosynthesis of Nucleotides
Survey
Document related concepts
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
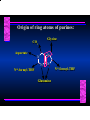
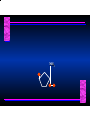
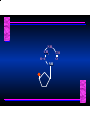
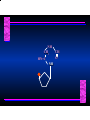
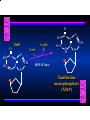
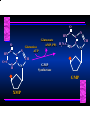
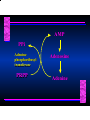
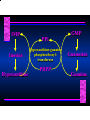
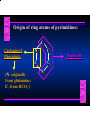
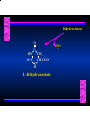
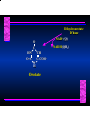
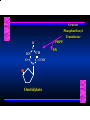
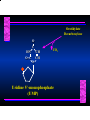
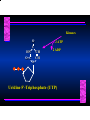
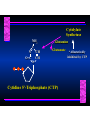
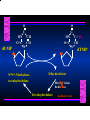
Biosynthesis of Nucleotides Nucleotides actively participate in many biochemical reactions: • ATP and GTP as energy sources • Uridine derivatives of sugars participate in carbohydrate metabolism • Coenzymes (NAD, FAD, CoA) are nucleotide derivatives • [ATP], [ADP], [AMP] act as allosteric regulators of key enzymes • Monomeric units of nucleic acids Two Pathways for Nucleotide Biosynthesis: de novo pathway (anew; from scratch): nucleotides are constructed from simple precursors salvage pathways: recovery and recycling of nucleotides obtained in the diet De Novo Biosynthesis of Purines: Studied first in pigeons. Birds excrete nitrogen as the purine uric acid: O H N O H N O N H N H Pigeons were fed isotopically labeled compounds and the distribution of labeled atoms examined in uric acid. Origin of ring atoms of purines: Glycine CO22 Aspartate 66 55 N 11 22 N33 44 N77 88 N99 10 10 N -formyl-THF Glutamine 10-formyl-THF N10 Atoms forming the purine ring are successively added to ribose-5-P. Purines are thus directly synthesized as nucleotide derivatives by assembling the atoms comprising the purine ring directly on ribose. Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) is formed from ribose-5-P and ATP by PRPP synthetase. PRPP is the donor of the ribose ring of the nucleotides. PRPP also participates in pyrimidine biosynthesis and in the synthesis of histidine and tryptophan. PRPP PRPP NH NH22 NH22 CH22 CH O=C O NH NH NH CH22 HN=C NH NH CH O N HC C H22N CH N N -OOC H22N N C C CH N N COOHC-NH CH22 COO- O C H22N N C C CH N N O H22N C H22N N C C CH N N O H22N C O=CH-NH N C C CH N N Inosine Monophosphate (IMP) O HN HC C N N C C CH N N AMP and GMP are synthesized from IMP -- OOC-CH22-CH-COO-NH N C N C CH C Adenylosuccinate HC N Synthetase N N IMP O HN HC C N N C C CH N N GDP, Pi aspartate GTP Adenylosuccinate N NH22 C HC OOC-CH22-CH-COO fumarate N NH N C N C Adenylosuccinase CH C HC N N N -- -- N C C AMP CH N N O HN IMP NADH O HN HC C N NAD++ N C C CH O=C C N H N C C CH N N IMP D’hase N N Xanthosine monophosphate (XMP) O HN O HN O=C Glutamine N ATP C N H C C C Glutamate AMP, PPi H22N-C N N C C CH N N CH N N GMP Synthetase GMP XMP Regulation of Purine Biosynthesis: • PRPP synthetase is feedback inhibited by AMP, GMP and IMP. • Adenylosuccinate synthetase is inhibted by AMP. • IMP d’hase is inhibited by XMP and GMP. Purine Salvage: • During cellular metabolism and during digestion in animals, nucleic acids are degraded to mononucleotides, nucleosides, and free purine bases. • Some purines are further degraded to uric acid, but a considerable fraction are directly converted back to purine ribonucleotides AMP PPi Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase PRPP Adenosine Adenine IMP Inosine Hypoxanthine GMP PPi Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase PRPP Guanosine Guanine Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: • Described by William Nyhan and Michael Lesch in 1964. • Hereditary deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Disease affects mostly males. • Hypoxanthine and guanine are degraded to uric acid instead of being converted to IMP and GMP. • Symptoms: mental retardation; spasticity; bizarre tendency to self-mutilate. Pyrimidine Biosynthesis • The common pyrimidine ribonucleotides are cytidine-5’-monophosphate and uridine-5’-monophosphate • The pyrimidine ring is synthesized first, then attached to ribose-5-phosphate • Pyrimidine nucleotides are made from aspartate, PRPP and carbamoyl phosphate Origin of ring atoms of pyrimidines: C 4 4 Carbamoyl Phosphate (N33 originally from glutamine; C22 from HCO33--) N 3 3 C 5 C2 C6 5 N1 Aspartate Glutamine + HCO33 + 2 ATP Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthase II (committed step in mammals) O H22N-C-OPO332-2- + Carbamoyl Phosphate 2 ADP, Pi Aspartate transcarbamoylase Aspartate + carbamoyl phosphate -- O -C =O CH22 H22N O=C CH-COO-N H N-carbamoylaspartate *ATCase was the first allosteric enzyme to be characterized Dihydroorotase O C CH22 HN O=C H22O CH-COO-- N H L-Dihydroorotate Dihydroorotate D’hase NAD++ (Q) O C CH HN O=C NADH (QH22) C-COO-- N H Orotate Orotate Phosphoribosyl Transferase PRPP O C CH HN O=C C-COO-N Orotidylate PPi Orotidylate Decarboxylase O C HN CH O=C CH CO22 N Uridine 5’-monophosphate (UMP) Kinases O C 2 ATP HN CH O=C CH 2 ADP N Uridine 5’-Triphosphate (UTP) Cytidylate Synthetase NH22 C CH N O=C Glutamine Glutamate CH N Cytidine 5’-Triphosphate (CTP) *Allosterically inhibited by CTP Mammalian pyrimidine synthesis is an example of metabolite channeling. In bacteria, the six enzymes of de novo pyrimidine synthesis are separate proteins. In mammals, the six activities are contained within three proteins. CPS-II, asparate transcarbamoylase, dihydroorotase are all contained within a single cytosolic protein. DHO d’hase is localized in the inner mito. membrane. Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and OMP decarboxylase are contained with a single protein called OMP synthase. Regulation of Pyrimidine Biosynthesis: • Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II is allosterically activated by PRPP and ATP. Pyrimidine nucleotides (UDP, UTP) inhibit. • Aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) from E. coli is inhibited by pyrimidine nucleotides (CTP and UTP). ATP is an allosteric activator. • Deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized by reduction of ribonucleosides • All 4 ribonucleoside diphosphates (ADP, GDP, CDP, UDP) are substrates for Ribonucleotide Reductase • Ribonucleotide Reductase has both a catalytic site and two allosteric sites. One allosteric site (Activity site) controls activity at the catalytic site. The second (Specificity site) determines which nucleoside diphosphate binds the active site. Ligand Ligand bound bound to to Activity Activity Site Site dATP Ligand Ligand bound bound to to Specificity Specificity Site Site Activity Activity of of Catalytic Catalytic Site Site Enzyme Inactive CDP or UDP ATP ATP or dATP ATP dTTP GDP ATP dGTP ADP dTMP is formed from dUMP: UMP UDP dUDP dUTP Nucleoside Ribonucleotide Nucleoside Monophosphate Reductase Diphosphate Kinase Kinase dTMP Thymidylate Synthase dUMP dUTPase dTMP is also formed from dCDP: dCDP dCMP dUMP Cytidine deaminase (activated by dCTP inhibited by dTTP) Of the 4 dNTPs, only dCTP does not interact with the regulatory sites on ribonucleotide reductase, instead it interacts with dCMP deaminase. O C dUMP O C HN CH HN O=C CH O=C N 10-MethyleneN55N10 tetrahydrofolate C-CH33 CH N Dihydrofolate Dihydrofolate Reductase X Tetrahydrofolate methotrexate dTMP dTMP can also be synthesized via salvage of thymidine: Thymidine ATP ADP Thymidine kinase dTMP Radioactive thymidine is used for monitoring intracellular synthesis of DNA because it enters cells easily and its principle metabolic fate is salvage leading to incorporation into DNA. • Many anticancer drugs target DNA synthesis; particularly thymidylate synthesis • Methotrexate and aminopterin inhibit dihydrofolate reductase; thymidylate cannot be formed thus DNA cannot be replicated • 5-Fluorouracil is converted to 5-Fluorodeoxyuridylate which binds tightly to thymidylase synthase and inhibits the enzyme. • Azaserine and acivicin are glutamine analogues also used as chemotheraputic agents