* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 (part 2)
Chloroplast DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Chromatography wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
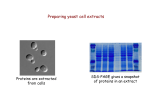
Chapter 3 (part 2) Protein purification and Analysis Why purify proteins? • Pure proteins are required to study enzyme function • Pure proteins are required for structural analysis (x-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy) • Pure proteins are required to obtain amino acid sequence Steps in protein purification • Develop assay • Choose source of protein • Prepare tissue extract – cell disruption – subcellular fractionation • Protein fractionation (several steps) • Determination of purity Differential Centrifugation transfer supernatant 1000 g tissue homogenate 10,000 g Pellet unbroken cells nuclei chloroplast transfer supernatant transfer supernatant 100,000 g Pellet mitochondria Pellet microsomal Fraction (ER, golgi, lysosomes, peroxisomes) Super. Cytosol, Soluble enzymes Chromatography Gel Permeation Chromatography Ion-exchange Chromatography +++ --- +++ ----+ + +++ + ++ + + ++ + ++ + ++ + + + ++ ++ + ++ + + ++ + ++ + ++ + + + ++ low salt buffer high salt buffer ++ +- ++- -+ + + ++ --- + -+ Cl Cl+- + +- + Cl- + ++ + +Cl + + Cl+- + +Cl+ + ++ ++ + ++ + + ++ + ++ + ++ + + + ++ ++ + ++ + + + ++ +++ +++ ++ - +- +++ + + ++ ++ + ++ + + + ++ +++ --- --- --- Affinity Chromatography Add excess ligand SDS poly acrylamide electrophoresis (PAGE) SDS = H3C-(CH2)10-CH2-OSO3- SDS – denatures protein coats w/ negative charge --- -- - - - -- --- Used to determine protein MW And purity of protein prep Isoelectric Focusing pH 3 Decreasing pH - Decreasing pH pH 9 + + 2-D Electrophoresis Decreasing MW large Decreasing pH Decreasing MW SDS-PAGE small + Decreasing pH Amino Acid Analysis 1) Acid hydrolyze protein 2) Treat with phenylisothiocyanate (PICT) N C S + H3N H O C C S C HN O- R C N C O 3) Separate derivatized AA’s by HPLC R H Protein Sequencing (Edman Degradation) C S N H3N O C C NH R 2) N S H O C HN C C O C C X R NH R Trifluoroacetic acid H H O C C X R S C HN 3) C N C R H + 2HN H O C C X R O Can sequence in 30 to 60 AA’s from N-terminus Repeat 1) H Generate Proteolytic Fragments Endopeptidases •Typsin •Chymotrypsin cleaves at COOH end of Lys and Arg cleaves at COOH end of Phe, Tyr, Trp Chemical Cleavages •Cyanogen Bromide cleaves at COOH end of Met Generate overlapping fragments Sequence individual fragments and piece together sequence Peptide mapping exercise Met-Ala-Arg- Gly-Glu-Tyr-Met-Cys-Lys-Phe-Ala-Glu-Gln-Asp Trypsin Met-Ala-Arg Phe-Ala-Glu-Gln-Asp Gly-Glu-Tyr-Met-Cys-Lys Chymotrysin Met-Ala-Arg- Gly-Glu-Tyr Met-Cys-Lys –Phe Ala-Glu-Gln-Asp CNBr Met Ala-Arg-Gly-Glu-Tyr-Met Cys-Lys-Phe-Ala-Glu-Gln-Asp Proteomic Analysis Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF)