* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Point
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
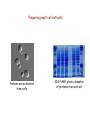
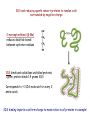
Preparing yeast cell extracts Proteins are extracted from cells SDS-PAGE gives a snapshot of proteins in an extract There are major challenges in analyzing yeast cell proteins! How can proteins be efficiently extracted without being degraded? Tough cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane Vacuoles contain multiple proteases Christopher Bruser, www.celllibrary.org used with permission Our procedure depends on the rapid and efficient extraction of yeast proteins Proteins are denatured during the process What happens during denaturation? Proteins are stabilized by thousands of bonds Vast majority are non-covalent: ionic, polar, hydrogen, van der Waals Covalent disulfide bonds link cysteines Proteins are extracted under denaturing conditions: • heat • denaturing detergent (SDS) • sulfhydryl reagent (2- aka β-mercaptoethanol) Sodium dodecyl sulfate is a denaturing detergent with multiple roles in extract preparation Detergents are amphipathic molecules that render hydrophobic molecules soluble in aqueous solutions Long side chain binds hydrophobic regions in proteins and cell membranes Hydrophilic head group binds water molecules SDS and reducing agents convert proteins to random coils surrounded by negative charge 2-mercaptoethanol (β-Me) reduces disulfide bonds between cysteine residues SDS binds and solubilizes unfolded proteins: 1 gram protein binds 1.4 grams SDS Corresponds to ~1 SDS molecule for every 2 amino acids SDS binding imparts a uniform charge to mass ratios to all proteins in a sample! “Quick and dirty” protein extraction from yeast 1. Collect cells by centrifugation 2. Wash cells with deionized water 3. Treat cells with 0.2 N NaOH for 5 minutes (weakens membrane without lysing the cells) 4. Resuspend the cells in 2X SDS-PAGE sample buffer and boil IMMMEDIATELY for 3 minutes. (Note: do NOT centrifuge the samples.) 5. Store the samples in the freezer until used for SDSPAGE.