* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dehydration of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol to make alkenes March 1 & 3
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
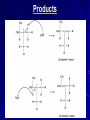
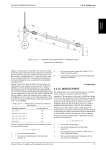
Synthesis of Alkenes 1: Miniscale Synthesis of Alkenes Via the Acid-catalyzed Dehydration of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol C C Organic Chemistry Lab II, Spring 2009 Dr. Milkevitch March 1 & 3, 2010 Elimination Reactions Today: Conduct an elimination reaction – One of the fundamental reactions of organic compounds What you will learn/observe: Review elimination reactions Learn how to synthesize an alkene – Acid catalyzed dehydration of an alcohol Look at the products formed See which product will predominate Elimination Reactions Let’s Review: – Elimination reaction: a fundamental organic reaction Two species are eliminated from a substrate Elimination mean’s they are gone, gone, gone – NOT a substitution Basic mechanism: Another Kind of Elimination Reaction A dehydration reaction – Multiple step reaction – Loss of water, forming a carbocation – Alkene formation results Mechanism: E1 mechanism – E1 elimination of a protonated alcohol Reaction of alcohols – Acid catalyzed – Forms an alkene and water General Mechanism: Acid-Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol Step 1: Protonation of hydroxyl group Step 2: Ionization to carbocation Step 3: Deprotonation to give the alkene Mechanism for This Reaction Step 1: Protonation of the alcohol Step 2: Formation of the carbocation Rearrangement Hydrogens available for elimination Products Products: Don’t Forget Formed from secondary carbocation Which Product Prevails? •More substituted alkene predominates •Called Zaitsev’s Rule Procedure Construct your simple distillation apparatus Use a 25 ml RB flask Place 6 ml of 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol into this flask – Include a magnetic stir bar Add 6 ml of 85% phosphoric acid to this flask Place on apparatus Start stirring and heating Collect distillate in a graduated cylinder – In an ice bath Distillate should be cloudy Don’t let the temperature rise above 75 deg C!! Procedure II Complete distillation Turn off heat, let apparatus cool Disassemble distillation apparatus – Clean with acetone – Set aside to dry Transfer distillate to a small separatory funnel – Drain lower aqueous layer into a beaker Wash organic layer with 20 ml of saturated salt soln Drain off lower aqueous layer Pour off organic layer into a 25 ml erlenmeyer flask Dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate Procedure III Gravity filter into a clean, dry 10 ml RB flask Reassemble distillation apparatus Distill again – Cool receiving flask in an ice bath Weigh a small vial, record weight of this flask When distillation is done, transfer distillate to this vial Reweigh the distillate in the vial Do a GC analysis – Determine the % of your alkenes – Determine the % of your starting material (3,3-dimethyl-2butanol) Accomplish a IR spectrum Your Report Formal Report Required Make sure to include the mechanism of the reaction in your report (separate section) Results Section: – Make sure to state all results Prove that you made the alkenes – Include GC chromatogram (annotated) – Determine % of your alkenes – IR spectrum, annotated (if completed) Conclusions section: – Was the experiment successful? How much of the alkenes are produced? Any leftover 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol? – If unsuccessful, any ideas why? Miniscale Apparatus for Distillation