* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
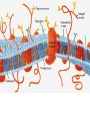
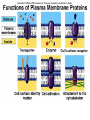
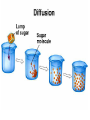
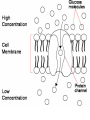
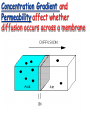
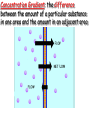
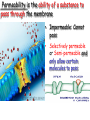
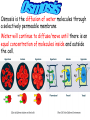
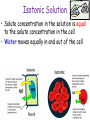
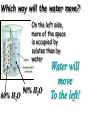
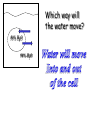
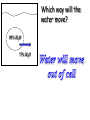
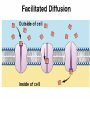
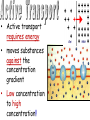
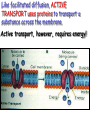
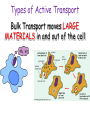
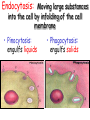
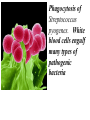
Cell Membrane Structure & Transport All cells need to exchange substances like food, water, and nutrients with their environment Cell membranes accomplish this exchange through cell transport! Why is the membrane’s structure described as a “fluid mosaic”? • Membranes are fluid and have the consistency of vegetable oil • The lipids & proteins are always in motion • Proteins form patterns or mosaics • Cell Membrane is composed of – Phospholipid bilayer: forms the basic unit of the cell membrane – Proteins: help transport large molecules through the membrane – Carbohydrates: help cells send and receive chemical messages Phosphate heads interact with water: Hydrophilic Lipid tails repel water: Hydrophobic 2 Main Types of Cell Transport • Passive Transport: NO energy required • Active Transport: NEEDS energy Passive Transport: Movement of materials across the membrane that does not require energy 3 Types: Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration until they are evenly spread out Hi to the Low YO! Concentration Gradient and Permeability affect whether diffusion occurs across a membrane Concentration Gradient: the difference between the amount of a particular substance in one area and the amount in an adjacent area Permeability is the ability of a substance to pass through the membrane • Impermeable: Cannot pass • Selectively permeable or Semi-permeable and only allow certain molecules to pass Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane Water will continue to diffuse/move until there is an equal concentration of molecules inside and outside the cell. 17 Hypertonic Solutions • Solute concentration outside of the cell is higher than the solute concentration inside the cell • Water moves OUT of the cell 19 Hypotonic Solutions • Solute concentration outside of the cell is lower than the solute concentration inside the cell • Water moves INTO the cell 20 Isotonic Solution • Solute concentration in the solution is equal to the solute concentration in the cell • Water moves equally in and out of the cell 21 Which way will the water move? On the left side, more of the space is occupied by 22 solutes than by water 60% H2O 90% H2O Which way will the water move? 80% H2O 100% H2O What type of solution is this cell in? 80% H2O 100% H2O Which way will the water move? 90% H2O 90% H2O 90% H2O 90% H2O What type of solution is this cell in? Which way will the water move? 90% H2O 75% H2O What type of solution is this cell in? 90% H2O 75% H2O Some things like glucose and proteins are too large to pass though the membrane by diffusion or osmosis Carrier proteins transport (diffuse) large substances across the membrane from high to low concentration • Active transport requires energy • moves substances against the concentration gradient • Low concentration to high concentration!! Like facilitated diffusion, ACTIVE TRANSPORT uses proteins to transport a substance across the membrane. Active transport, however, requires energy! Types of Active Transport Bulk Transport moves LARGE MATERIALS in and out of the cell Endocytosis: Moving large substances into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane • Pinocytosis: engulfs liquids • Phagocytosis: engulfs solids Amoebas take in food and nutrients through phagoctosis…... Phagocytosis of Streptococcus pyogenes. White blood cells engulf many types of pathogenic bacteria Exocytosis: Large substances are shipped out of the cell by outfolding of the cell membrane Think “exit”