* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusionosmosis07 - McCarthy`s Cool Science
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
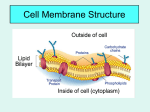
Assignment # Diffusion and Osmosis Mrs. McCarthy Biology May 22, 2017 I. The Cell A. In order to live, a cell must take in nutrients and water and eliminate wastes B. Parts of the cell involved in diffusion and osmosis: 1. Cell membrane – a semipermeable membrane that allows some small molecules through, but blocks others. Water is able to pass through freely. The Cell Membrane I. The Cell 2. Cytoplasm – the jelly like substance in the cell that is composed of mainly water and dissolved solutes. II. The movement of Substances Into and Out of Cells A. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration 1. Diffusion stops when equilibrium (balance) is reached Diffusion causes the molecules to move from area A to area B Diffusion causes the molecules to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration II. The movement of Substances Into and Out of Cells B. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across the cell membrane 1. The water will move from an area of low solute to an area of high solute until equilibrium is reached. (The water wants to evenly dilute the solute) In osmosis, the water will move towards the solute to dilute it evenly. Osmosis III. Types of solutions A. Hypertonic – the concentration of solutes outside the cell is greater than it is inside. 1. Water will move outside the cell to dilute the higher concentration of solutes 2. The cell will shrink Hypertonic Solution IV. Models of Different Solutions (turn to the back) A. A cell in a HYPERTONIC SOLUTION X = NaCl (salt) O = H2O X O X X O X O O O X X X X X O X X X XO X O O O X X III. Types of solutions B. HypOtonic – the concentration of solutes inside the cell is greater than it is outside 1. Water will move inside the cell to dilute the higher concentration of solutes 2. The cell will SWELL (unless the water is pumped out by a contractile vacuole) HypOtonic solution IV. Models of Different Solutions (turn to the back) A. A cell in a HYPOTONIC SOLUTION X = NaCl (salt) O = H2O O O X O O X X O OXX O O O O X X O X O X O XO O O The contractile vacuole in single celled organisms pumps out excess water so the cell does not burst III. Types of solutions C. Isotonic – the concentration of solutes inside and outside the cell is the same 1. Water will not move 2. The cell will stay the same Isotonic solution IV. Models of Different Solutions (turn to the back) A. A cell in a ISOTONIC SOLUTION X = NaCl (salt) O = H2O X O O O X O X O X O O X O X X X O X O X Journal Entry # 1. Explain the difference between osmosis and diffusion. 2. Explain this cartoon using the terms osmosis, hypertonic, and diffusion. Classwork Complete the Diffusion and Osmosis practice worksheet. Be sure to read all directions very carefully.