* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - SchoolRack
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
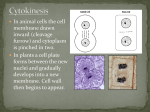
Chapter 5 The Cell in Action Section 1: Exchange with the Environment A cell must be able to obtain energy and raw materials and get rid of wastes This exchange of materials takes place at the cell’s membrane What is Diffusion? Matter is made up of tiny particles Particles of matter are always moving and colliding with each other Particles naturally travel from areas where they are crowed to areas where they are less crowded - diffusion Diffusion - the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Diffusion of Water All organisms need water to live Cells are surrounded by and filled with fluids (mostly water) The movement (diffusion) of water through the cell membrane is called osmosis Because osmosis is diffusion, water moves from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration Like animal cells, plant cells also take in and release water by osmosis What would happen to a grape if you placed it in a dish of pure water? What would happen to it if you placed it in water mixed with a large amount of sugar? Moving Small Particles Many particles are too large to “slip” past the molecules of the cell membrane i.e. amino acids and sugars must pass through protein “doorways” located within the membrane They can travel through these proteins either by passive or active transport Passive transport - is the diffusion of particles through membrane proteins This does not require energy Active transport - is the movement of particles through membrane proteins against the normal direction of diffusion This requires energy (ATP) Moving Large Particles The cell can also move particles into and out of the cell that are too large to pass through membrane proteins Endocytosis - when the cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses it in a vesicle Exocytosis - vesicles are formed carrying particles to the cell membrane to be removed Section 2: Cell Energy Why do you get hungry? Feeling hungry is your body’s way of telling you that your cells need energy FROM SUN TO CELL All energy that fuels life comes from the sun Plants are able to capture the energy of the sun and store it in sugars (glucose) Photosynthesis The process of capturing light energy and changing it into food is called photosynthesis Photosynthesis means “made by light” Plants have molecules in their cells that capture light - pigments Chlorophyll - the main pigment found in plant cells Chlorophyll is found in the chloroplasts http://www.hsv.k12.al.us/schools/middle/wtms/student/cell/cell_energy.html Plants use the energy captured by chlorophyll to change carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H20) into food (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2). Glucose (C6H12O6) is a carbohydrate. The glucose can be used by the plant or stored as energy in the form of other carbohydrates or lipids. Getting Energy from Food Cells get energy from the food you eat But they can’t get it directly from a banana or a piece of pizza All organisms must break down food molecules in order to release energy There are two ways to do this: 1) Cellular Respiration 2) Fermentation Cellular Respiration Most organisms use cellular respiration to obtain energy that is stored in food C.R. breaks down glucose, in the presence of oxygen, into carbon dioxide and water, which releases energy This energy is then converted and stored as ATP, which is eventually used by the cells Does the equation for respiration remind you for the equation for photosynthesis? Let’s take a look Fermentation Have you ever run so far or fast that your muscles start to burn? This happens because your muscle cells can’t get the O2 it needs to produce ATP by cellular respiration Your body then uses fermentation Fermentation leads to the production of a small amount of ATP There are two types: 1) Lactic Acid - occurring in your muscles 2) Alcoholic - occurring in bacteria and yeast Section 3: The Cell Cycle In the time it takes you to read this sentence, your body will have produced a millions of new cells! Producing new cells allows you to grow and replace cells that have died i.e. The environment in your stomach is so acidic that the cells lining it have to be replaced every week! The Life of a Cell Cell cycle - the life cycle of a cell The cell cycle begins when the cell is formed and ends when the cell divides to form a new one Before a cell divides it must make an exact copy of all its DNA and organelles DNA in a cell is organized into structures called chromosomes Making More Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) and their DNA are not very complex Bacteria have ribosomes and a singular circular DNA Because of this division of bacteria cells is simple - binary fission Binary fission means “splitting in two” Eukaryotic Cells and Their DNA Eukaryotic cells are much larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells Because of this eukaryotic cells have a lot more DNA The total number of chromosomes in eukaryotic cells varies from organism to organism i.e fly - 8, potato - 48, and human - 46 (23 pairs) Pairs of similar chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes Making More Eukaryotic Cells The eukaryotic cell cycle has three main stages In the first stage, the cell grows and copies its organelles and chromosomes (DNA) After each chromosome is duplicated, the two copies are held together at a region called the centromere and are called chromatids In the second stage, the chromatids separate The complicated process of chromosome separation is called mitosis Mitosis ensures that each new cell receives a copy of each chromosome Mitosis can be divided into four phases In the third stage of the cycle, the cell divides and produces two cells that are identical to the original cell Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Although mitosis is a continuous process, it can be divided into four phases; Phase 1 - prophase Phase 2 - metaphase Phase 3 - anaphase Phase 4 - telophase Before Mitosis Before mitosis begins, the chromosomes, organelles, and centrioles are copied. Each chromosome now consists of two chromatids Mitosis Phase 1 The nuclear membrane breaks apart The two centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell Fibers form from the centrioles and attach to the centromeres Mitosis Phase 2 The chromosomes line up in the middle (equator) of the cell Mitosis Phase 3 The chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite sides of the cell by the fibers attached to the centrioles Mitosis Phase 4 A nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes The fibers disappear Mitosis is complete Cytokinesis In eukaryotic cells that do not have a cell wall, division of the cytoplasm begins at the cell membrane The cell membrane will eventually pinch all the way through the cell until there are two In eukaryotic cells with a cell wall, a cell plate forms in the middle of the cell and becomes the new cell membranes that will separate the cell. Once the cell is split a new cell wall forms http://bhs.smuhsd.org/bhsnew/aca demicprog/science/vaughn/Studen t Projects/Paul & Marcus/Cell_Replication.html