* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 11 Biology DP Assignment 3 Cells
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
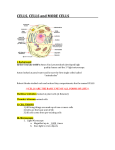
Grade 11 Biology DP Assignment 3 Cells The History of the Cell Theory • Before microscopes were invented, people believed that diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits. • As scientists began using microscopes, they quickly realized they were entering a new world–one of microorganisms. • Microscopes enabled scientists to view and study cells, the basic units of living organisms. The cell theory is made up of three main ideas: All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms. All cells come from preexisting cells. Development of Electron Microscopes There are two basic types of electron microscopes. The scanning electron microscope scans the surface of cells to learn their three dimensional shape. The transmission electron microscope allows scientists to study the structures contained within a cell. All living cells must maintain a balance regardless of internal and external conditions. Survival depends on the cell’s ability to maintain the proper conditions within itself. It is the plasma membrane’s job to: • allow a steady supply of glucose, amino acids, and lipids to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. • remove excess amounts of these nutrients when levels get so high that they are harmful. • allow waste and other products to leave the cell. This process of maintaining the cell’s environment is called homeostasis. Selective permeability is a process used to maintain homeostasis in which the plasma membrane allows some molecules into the cell while keeping others out. It is fluid because the phospholipid molecules move within the membrane. Proteins in the membrane that move among the phospholipids create the mosaic pattern. A prokaryotic cell does not have internal organelles surrounded by a membrane. Most of a prokaryote’s metabolism takes place in the cytoplasm. 2. DNA 1. Ribosomes 3. Plasma membrane 4. Cell wall This eukaryotic cell from an animal has distinct membrane-bound organelles that allow different parts of the cell to perform different functions. 1. Nucleus 2. Nucleolus 3. Chromosomes 4. Plasma membrane 5. Organelles