* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
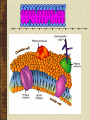
Cells Coach Kirkpatrick Biology Text: Biology: Principles and Explorations Cell Theory All living things are composed of 1 or more cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function. Cells come only from existing cells. Cell Organization Prokaryotes: Organisms whose cells do NOT have a nucleus. This includes ONLY bacteria. Eukaryotes: Organisms whose cells contain a nucleus. Includes both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Everything except bacteria. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) Does not dissolve in watery environment of the body. The membrane is nonpolar but the environment of the body is polar. The chemical composition is not the same so it’s like mixing oil and water. Consists of a lipid bilayer made up of polar heads and nonpolar tails. This lipid bilayer is chemically composed of phospholipids. Phospholipids are compounds containing phosphorus and fatty acids. Cell Parts Cytoplasm: Jelly-like fluid in the interior of the cell. Contains organic salts, minerals and water. Organelles: Specialized parts or compartments with special functions. Prokaryotes do not have organelles, ONLY eukaryotes. Other organelles include those on your cell function cards. Microscopes Light Microscopes: Uses lights and various lenses to help magnify objects. SEM: Scanning electron microscopes use electrons to create a 3-D image as electrons bounce off the surface of specimens. TEM: Tunneling electron microscopes use electrons, but they pass through specimens to form an image.