* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5-3
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
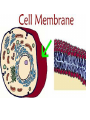
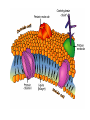
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
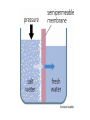
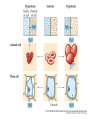
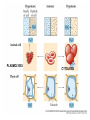
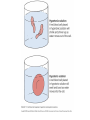
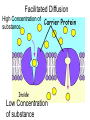
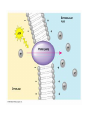
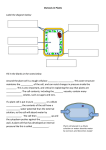
Chapter 5-3 Maintaining a Constant Cell Environment CELL MEMBRANE • “Gate-keeper”- helps regulate what enters and leaves the cell • __________ process by which a stable internal environment is kept Balloon Demonstration • Smell the balloon- what do you observe? • Why is this possible? Cell Membranes • Cell membranes are selectively permeable- some things pass through easily and others do slowly or not at all • Particles are always moving • Move in straight lines in all directions • Collide with each other • Diffusion: movement of molecules or particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration • Concentration gradient: difference in concentration between two areas Osmosis • OSMOSIS: diffusion of water across selectively permeable membrane from high water concentration to low water concentration • Osmosis Animation Osmosis • Which has a higher water concentration? 100 mL of pure water or 100 mL saltwater? ANSWER: There are more water molecules in pure water because salt takes up volume Three types of solutions: • Hypertonic solution: higher concentration of solutes than the cell • Hypotonic solution: lower concentration of solutes than the cell • Isotonic solution: same concentration of solutes as the cell Effects of Osmosis • Effects of Osmosis Turgor Pressure Turgor (osmotic) pressure- Force exerted outward by the water contained in the cell. • All cells experience this Effects of Osmosis • Plasmolysis- shrinking of cytoplasm caused by osmosis – What type of solution causes this? • Cytolysis- cell bursts due to too much caused by osmosis – What type of solution causes this? PLASMOLYSIS CYTOLYSIS Cell membrane • Composed of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates • Made up of two layers sandwiched together • Parts of the membrane are actually “fluid” and move Functions of proteins • Transport proteins- allow materials that can’t directly go through membrane to get into the cell • Receptor- communication for the cell • Enzymes • Structural – connect to other cells or to structures inside cell Selective permeability • Lipid molecules • Small molecules- water glucose, amino acids, CO2, oxygen • What passes through is based on chemical properties of membrane and substance trying to get in Facilitated Diffusion • Facilitated Diffusion- transport of substances across membrane through transport proteins • Specific to substate Facilitated Diffusion High Concentration of substance Low Concentration of substance Passive and Active Transport • Passive transport – diffusion down a concentration gradient without using energy from cell – EXAMPLE: Like riding the bike down the hills high concentration Low concentration • Active Transport- movement of materials against a concentration gradient – Riding a bike up a hill Low concentration high concentration Why do cells need active transport? • Maintain different internal conditions than would occur naturally • Creating a large gradient can use this for work – Use to generate energy – Conduct nerve impulses – Concentrate substances Two forms of active transport