* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells PPt
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
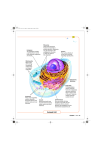
THE CELL The Cell Theory 1. All living organisms are made of cells. Protist cells Skin cells Bacteria cells Plant cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. Red Blood Cells Skin Cells Nerve Cells Their shape relates to their job! 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. Two Types of Cells • Prokaryote- simple cell without a nucleus or membrane bound organelles • Ex. • Archeabacteria • Eubacteria Two Types of Cells • Eukaryotecomplex cell with a well defined nucleus and membrane bound organelles • Ex. Plants and animals Present in all cells 1. Cell Membrane Present in all cells 2. Cytoplasm Present in all cells 3. Ribosome 4. DNA DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Animal Type of Cell Eukaryotic Organelles and Cell Parts Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Ribosomes Vacuole Vesicles • Lysosome • Centrioles Plant Eukaryotic Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Ribosomes Vacuole Vesicles • Central Vacuole • Cell Wall • Chloroplast Cell Membrane Controls what enters and exits the cell The Organelles • Microfilaments & Microtubules * Provide support, the cytoskeleton (movement of organelles. Nucleus Control center of the cell…acts like the brain or boss. Contains cell’s DNA The Organelles • Nucleolus * Produces ribosome The Organelles • Endoplasmic Reticulum * The cells transport system The Organelles • Ribosomes (free and attached) • Produce proteins *Think Ribs……UMMM! The Organelles • Golgi Body/Apparatus * Packages proteins Vesicles • Transports things around the cell like a vehicle does for us. The Organelles • Mitochondria * Cells energy producer (glucose ATP) The Organelles • Vacuole * Stores water and water soluble materials. The Organelles • Lysosome * Contains strong digestive enzymes The Organelles • Centrioles * Aid in moving chromosomes during cell division Cell Wall • Provides support and protection for the plant cell (RIGID) The Organelles • Chloroplast * Store chlorophyll for photosynthesis Cytoplasm • Jelly-like substance that holds organelles in place. Cytosol. LIMITS TO CELL SIZE • Must maintain a workable surface area to volume ratio (the volume increases faster than the surface area) • DNA can only “produce” a specific amount of protein • Rate of intracellular diffusion is inversely proportional to cell volume Cell Size Comparison on the internet http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/scale/