* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Functions
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
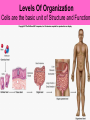
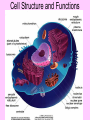
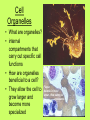
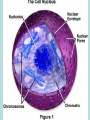
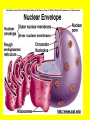
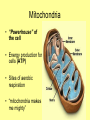
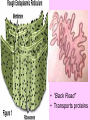
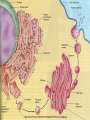
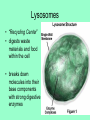
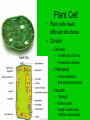
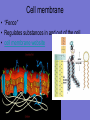
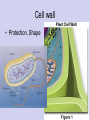
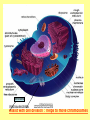
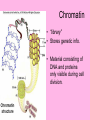
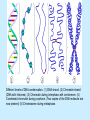
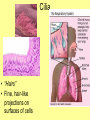
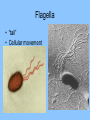
Is it made of cells? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Flowers Skin Proteins Rocks Milk Bone Lungs Hamburger DNA Calcium Apples Chromosomes Saliva atoms 15. Sand 16. Worms 17. Leaf 18. Water 19. Molecules 20. Sugar 21. Chlorophyll 22. Paramecium 23. Blood 24 Cell membrane 25. Mushrooms From Carbon to Coffee Bean Amazing Cells http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/ • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begi n/cells/scale/ From carbon to coffee bean Smallest-----Largest 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Carbon atom Adenine Glucose Phospholipid Antibody Ribosome Influenza virus E. coli Bacterium Mitochondria 10. Baker’s yeast 11. Sperm cell 12. RBC 13. Skin cell 14. Human Egg 15. Paramecium 16. Amoeba Proteus 17. Grain of Salt 18. Coffee Bean Levels Of Organization Cells are the basic unit of Structure and Function • What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Cell Structure and Functions Cell Theory There are three parts to the cell theory: 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. 3. All Cells arise from pre-existing cells Cell Organelles • What are organelles? • internal compartments that carry out specific cell functions • How are organelles beneficial to a cell? • They allow the cell to grow larger and become more specialized • Nucleus: “control center”; houses DNA; directs activities of the cell • Nucleolus: producing ribosomes • Nuclear envelope: “envelope”; encloses the nucleus and its contents • Nuclear pore: “door”, pore in nucleus; can allow substances (RNA) to leave Mitochondria • “Powerhouse” of the cell • Energy production for cells (ATP) • Sites of aerobic respiration • “mitochondria makes me mighty” Smooth endoplasmic reticulum • “Cell Highway” • Synthesizes steroids • Detoxifies poisons (alcohol) • Transports substances • Regulates calcium levels for muscle contraction • “Back Road” • Transports proteins Ribosomes • “Farmer” • Make proteins Golgi Apparatus • “Post Office” • membrane-bound structure • organelle modifies molecules and packages them into small membrane bound sacs called vesicles Vesicle • “Taxi” • Membrane-sac that transports materials • vesicle website Lysosomes • “Recycling Center” • digests waste materials and food within the cell • breaks down molecules into their base components with strong digestive enzymes How do plant cells differ from animal cells? Plant Cell • Plant cells have different structures • Contain: – Cell wall • “Great wall of China” • Protection & Shape – Chloroplast • “Green Machine” • Site of photosynthesis – Vacuole • “Garage” • Stores water • Large in plant cells, small in animal cells Cell membrane • “Fence” • Regulates substances in and out of the cell. • cell membrane website Cell wall • Protection, Shape Cytoplasm • “Juice, Gel” • Fluid portion of the cell • Suspends organelles centrioles Assist with cell division : helps to move chromosomes Chromatin • “library” • Stores genetic info. • Material consisting of DNA and proteins only visible during cell division. Different levels of DNA condensation. (1) DNA strand. (2) Chromatin strand (DNA with histones). (3) Chromatin during interphase with centromere. (4) Condensed chromatin during prophase. (Two copies of the DNA molecule are now present) (5) Chromosome during metaphase. • Microtubules • “Skeleton” • Part of cytoskeleton • Assist in cell division and provide internal support • Can combine with other proteins to form complex structures like cilia and flagella Cilia • “Hairs” • Fine, hair-like projections on surfaces of cells Flagella • “tail” • Cellular movement Peroxisome • “Garbage Disposal” • Produces H2O2 • Helps destroy unneeded substances. • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begi n/cells/insideacell/ • http://www.khanacademy.org/science/biolo gy/human-biology/v/parts-of-a-cell