* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
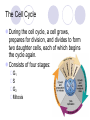
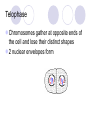
Mitosis ***DRAW ALL PICTURES*** The Cell Cycle During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells, each of which begins the cycle again. Consists of four stages: G1 S G2 Mitosis Cell Division and Definitions Before cell division begins, each cell must copy its DNA so that each daughter cell gets a complete copy of the genetic information. Mitosis: division of cell nucleus Cytokinesis: division of cytoplasm Chromosomes carry genetic information; made of DNA Not visible in most cells until cell division Mitosis Occurs in ALL eukaryotic cells except sex cells Broken down into the following stages: Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Interphase G1: growth phase S: chromosomes replicate G2: growth phase Prophase Chromatin condenses into chromosomes Centrioles separate and a spindle begins to form Nuclear envelope breaks down Metaphase Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere Anaphase Sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are moved apart. Telophase Chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell and lose their distinct shapes 2 nuclear envelopes form Cytokinesis The cytoplasm pinches in half Each daughter cell has an identical set of duplicate chromosomes. Animal cell pinches. Plant cell has a cell plate form between the two.