* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell-ebration Tutorial cell-ebration_tutorial
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
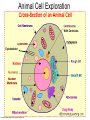
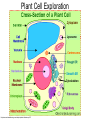
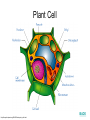
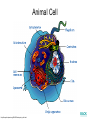
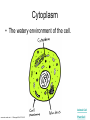
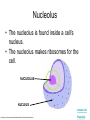
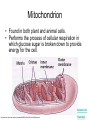
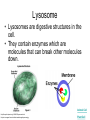
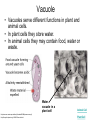
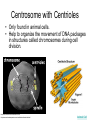
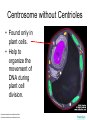
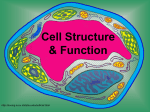
The Interactive Cell Tutorial Created by Samantha Ketover Kentridge High School October 2004 You have explored cell structures: • You have looked at 2 varieties of cells – Review questions to think about… 1. What are the two types? 2. What were the differences in organelles in each type? 3. What are the three parts of the Cell Theory? One or Many Cells • All organisms are made of one or many cells. • Organisms like the paramecium and amoeba are single celled. So are bacteria! • Organisms like humans, baboons, and plants are multi-celled. Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote • Cells can also be either prokaryote or eukaryote. • Prokaryotes are very simple organisms and have only one cell. • Eukaryotes are typically multi-celled and are more complex. Plant vs. Animal • Finally, cells can be either plant or animal in nature. • Plant cell • Animal cell Cells and Organelles • Cells are the basic units of form and function in living things. • Cells have forms (structures) inside them that do different jobs. These structures are called organelles. • Plant and animal cells have many organelles in common. Organelles in Common • Plant and animal cells both have: – – – – – – – – – – – – Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body Cytoskeleton Nucleolus Mitochondrion Lysosome Vacuole Centrosomes Each of these structures does a specific job for the cell! Organelles that are not in common: • Animal cells, but not plant cells have: – Centrosomes with Centrioles • Plant cells, but not animal cells have: – Chloroplasts – Cell walls Animal Cell Exploration With Centrioles Cytoskeleton http://www.allaboutsharks.com/subjects/animals/cell/ Plant Cell Exploration Lysosome Cytoskeleton http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/plants/cell/anatomy.GIF One Celled Organisms Paramecium http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html http://ebiomedia.com/gall/classics/Paramecium/paramecium1.html BACK Many Celled Organisms Sea anemone Lions and various plants http://www.sas.upenn.edu/African_Studies/Wildlife_GIFS/Anemo1_15513.gif http://www.sas.upenn.edu/African_Studies/Wildlife_GIFS/Safari_13280.gif BACK Prokaryotes • Only have one cell • Only have cell membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes and DNA. More on DNA later! BACK http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html Eukaryotes • Complex cells • Organism could be unicellular or multicellular • Eukaryotic cells have many cell parts! Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryote_examples.html BACK Plant Cell BACK http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal Cell BACK http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html • • • • Cell Membrane Forms the outer boundary of animal cells. Found inside the cell wall in plant cells. Determines what can enter and leave a cell. Made of protein and fat. Animal Cell http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html#The%20Cell%20Membrane Plant Cell Cytoplasm • The watery environment of the cell. Animal Cell www.ndsu.nodak.edu/.../ 135/images/CELLCYTO.GIF Plant Cell Nucleus • The command center of the cell. • Contains DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) the command molecule of the cell. • Surrounded by a membrane. Animal Cell http://ntri.tamuk.edu/cell/nucleus.html Plant Cell Ribosomes • Ribosomes are found attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) • Ribosomes are also found floating in the cytoplasm. • Their job is to make proteins that are molecules that help to build and repair cells. Animal Cell http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/animals/images/ribosome.jpg http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html#Endoplasmic%20reticulum Plant Cell Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) • The RER is responsible for modifying proteins that have been made by the cell. • It is rough because the RER membrane is studded with ribosomes. RER portion http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html#Endoplasmic%20reticulum Animal Cell Plant Cell Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) • The SER has membranes that are not covered in ribosomes. • The SER synthesizes or makes lipids for the cell. SER portion Animal Cell http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html#Endoplasmic%20reticulum Plant Cell Golgi Body, Apparatus, or Complex • The Golgi Body is responsible for doing the final modifications of proteins in the cell which are to be secreted. They molecularly tag the proteins for secretion. • The Golgi Bodies also produce lysosomes for the cell. Animal Cell Plant Cell Cytoskeleton • Forms the cell’s skeleton. • Made of microfilaments and microtubules which are protein-based structures. • Provides for the cell’s internal structure and also for cellular movement. Animal Cell http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html#Cell%20Movement Plant Cell Nucleolus • The nucleolus is found inside a cell’s nucleus. • The nucleolus makes ribosomes for the cell. NUCLEOLUS NUCLEUS Animal Cell http://www.cs.utexas.edu/users/s2s/latest/cell1/src/tutorial/nucleolus.html Plant Cell Mitochondrion • Found in both plant and animal cells. • Performs the process of cellular respiration in which glucose sugar is broken down to provide energy for the cell. Animal Cell http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookCELL2.html#Mitochondria Plant Cell Lysosome • Lysosomes are digestive structures in the cell. • They contain enzymes which are molecules that can break other molecules down. Animal Cell http://library.thinkquest.org/~C004535/lysosomes.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/animals/images/lysosome.jpg Plant Cell Vacuole • Vacuoles serve different functions in plant and animal cells. • In plant cells they store water. • In animal cells they may contain food, water or waste. Water vacuole in a plant cell Animal Cell http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/paramecvacs.gif http://library.thinkquest.org/~C004535/vacuole.html Plant Cell Chloroplast Elodea cells with chloroplasts • Only found in plant cells • Perform photosynthesis a process where glucose sugar and oxygen are made from carbon dioxide and water. http://ntri.tamuk.edu/cell/nucleus.html http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/130/Plant_Cell/Elodea/Cyto_strand_nucleus_MC.html Plant Cell Cell Wall • Only found in plant cells. • Made of a carbohydrate called cellulose • Provides structure and support for plant cells http://library.thinkquest.org/~C004535/cell_wall.html http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/130/Plant_Cell/Elodea/Cyto_strand_nucleus_MC.html Plant Cell Centrosome with Centrioles • Only found in animal cells. • Help to organize the movement of DNA packages in structures called chromosomes during cell division. http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/centriol.htm http://www.molecularexpressions.com/cells/animals/centrioles.html Animal Cell Centrosome without Centrioles • Found only in plant cells. • Help to organize the movement of DNA during plant cell division. http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/plntcell.htm http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/centriol.htm Plant Cell Cell Theory • All living things are made of cells. • Cells are the basic units of form and function in living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. BACK Nuclear Membrane • A double membrane that encloses genetic material in Eukaryotic cells • Separates contents of nucleus from cytosol • Many nuclear pores are present so that protein and genetic material may pass The End! Learn more at Cells Alive Try out an online quiz! Quia Cell Games The next question to explore… What are cells and their organelles made of?