* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document.
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
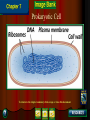
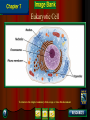
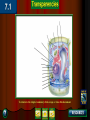
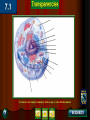
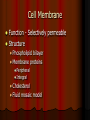
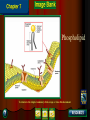
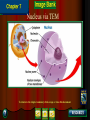
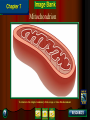
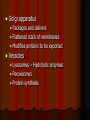
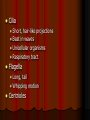
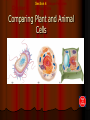
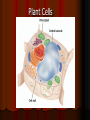
Chapter 4: The Cell Section 4-1: Introduction to the Cell Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1673) The cell theory Matthias Schleiden (1838) Theodor Schwann (1839) Rudolf Virchow (1855) Section 4-2 Introduction to Cells Cell Diversity Shape Determine function Size Limits: Surface area to volume ratio (Figure 4-5) Cells Basic Parts Plasma membrane Cytoplasm Control center Two types Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Human Cell To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Prokaryotic Cell To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Organization Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Multi-Cellular Organism To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Eukaryotic Cell To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Section 4-3 Cell Organelles and Features Cell Membrane Function - Selectively permeable Structure Phospholipid bilayer Membrane proteins Peripheral Integral Cholesterol Fluid mosaic model Phospholipid To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Phospholipid Molecules To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Membrane Proteins Peripheral Recognition Connections Receptors Integral Channels Pumps – carbohydrate chains Q.O.D. Which organelles are involved in protein synthesis and what is their role? The Nucleus Nuclear matrix Nuclear envelope Nuclear pores Chromatin/Chromosomes Nucleolus Nucleus via TEM To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. The Organelles Cytoplasm/Cytosol Mitochondria Function: energy (ATP) Structure: Double membrane Cristae – inner membrane Matrix and intermembrane space Contain own DNA Divide on their own Contain own ribosomes Mitochondrion To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Ribosomes Free or attached Made of proteins + RNA Function: Protein synthesis Enodplasmic Reticulum Structure: Membranous tubules and sacs Smooth ER vs. Rough ER Function depends on type of ER Endoplasmic Reticulum To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Q.O.D. What are the roles of the cytoskeleton? Golgi Apparatus To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. Golgi apparatus Packages and delivers Flattened stack of membranes Modifies proteins to be exported Vessicles Lysosomes – Hydrolytic enzymes Peroxisomes Protein synthesis Chapter 4 Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Processing of Proteins Cytoskeleton Functions Shape/Size Support Movement Structures Microfilaments - actin Microtubules Spindle fibers Cilia Short, hair-like projections Beat in waves Unicellular organisms Respiratory tract Flagella Long, tail Whipping motion Centrioles Section 4-4 Plant Cells Chapter 4 Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cells Plant Cells Cell Wall Support and protection Cellulose Primary/Secondary Vacuoles Storage Large, central Plastids Features: Own DNA, ribosomes Reproduce on their own Two membranes Types: Chloroplast Thylakoids Stroma and grana (granum) Chloroplast To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. The Chloroplast