* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Transport
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
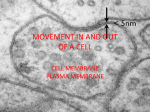
Cellular Transport Homeostasis • Cells respond to their environment to maintain homeostasis. • One way is to move substances across the cell membrane. Substances move across the Cell Membrane Proteins and Lipids Types of Transport • Passive Transport • Active Transport Diffusion or Passive Transport • Does NOT require energy. • Molecules move from high concentration to low concentration. • Molecules move with the concentration gradient. What’s happening? How would diffusion happen in a cell? How would diffusion happen in a cell? How would diffusion happen in a cell? How would diffusion happen in a cell? How would diffusion happen in a cell? How would diffusion happen in a cell? How would diffusion happen in a cell? How would diffusion happen in a cell? Osmosis is a type of diffusion Cell Membrane Osmosis is a type of diffusion Cell Membrane Osmosis is a type of diffusion Cell Membrane Osmosis is a type of diffusion Cell Membrane Osmosis is a type of diffusion (water) Cell Membrane Osmosis is a type of diffusion Cell Membrane Osmosis is a type of diffusion Cell Membrane Osmosis is a type of diffusion Cell Membrane HELP WANTED! Facilitated Diffusion I’m a Channel, I can help! Channel proteins help substances pass through the cell membrane. HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! HELP WANTED! I’m a Channel, I can help! Explain what is happening Explain what is happening Explain what is happening Explain what is happening Explain what is happening Explain what is happening Explain what is happening Explain what is happening How does Passive Transport affect my cells? What would happen to the animal cells in each beaker? 80% H2O 80% H2O 80% H2O 100% Distilled Water 80% Water 20% Dissolved Substances 70% Water 30% Dissolved Substances Which way did the water move? 80% H2O 100% Distilled Water Why did the cell get so big? Which way did the water move? 80% H2O 80% Water 20% Dissolved Substances Why did the cell stay the same size? Which way did the water move? 80% H2O 70% Water 30% Dissolved Substances Why did the cell get so small? REVIEW 1. Explain passive transport. 2. Explain diffusion. 3. Explain osmosis. 4. Explain facilitated diffusion. How is Active Transport different? 1. Active transport requires energy. 2. Molecules move from low concentration to high concentration 3. Molecules move against concentration gradient. Endocytosis • Bring in particles using cell membrane – There are 2 types: • Phagocytosis • Pinocytosis Phagocytosis Amoeba “Eats” large particles Pinocytosis “Cell Drinking” Brings in small particles or liquids Exocytosis How the cell gets rid of wastes REVIEW 1. Explain Active Transport. 2. How does a cell take in LARGE particles? 3. How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? 4. How does the cell get rid of wastes?