* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells 4 Quail
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
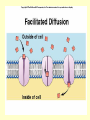
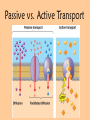
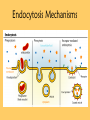
Questions of the Day • What are the four functions of proteins in the cell membrane? Goals • Understand and describe passive and active transport Passive Transport WITH the Gradient NO ATP NEEDED!!! Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion (channel/carrier proteins) Transport • A difference in the concentration of a substance across a space is called a concentration gradient. • Equilibrium is a condition in which the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a space. Diffusion • One way cells maintain homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across their cell membrane. • Cells must use energy to transport some substances across the cell membrane. – This is known as Active Transport • Other substances move across the cell membrane without any use of energy by the cell. AKA passive transport Diffusion • The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration caused by the random motion of particles of the substance is called diffusion. Osmosis • The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. • Like other forms of diffusion, osmosis involves the movement of a substance—water—down its concentration gradient. • Osmosis is a type of passive transport. Diffusion/Osmosis Active Transport ATP NEEDED!!! Endocytosis Against the Gradient Exocytosis Sodium-Potassium Pump Passive vs. Active Transport Active Transport in Action Endocytosis Mechanisms Exocytosis The “tonics”