* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells, you would be nothing without them!
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
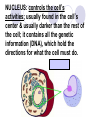
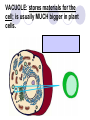
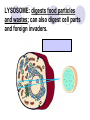
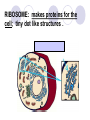
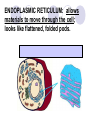
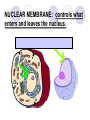
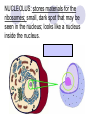
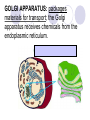
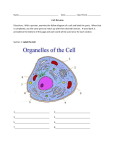
Cells, you would be nothing without them! Animal OR Plant? Animal OR Plant? The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure & function of living things. 3. Living cells come only from other cells. What’s inside a cell? ORGANELLE: a structure in a cell. CELL MEMBRANE: controls what enters and leaves the cell; it surrounds the cell. CYTOPLASM: allows materials to move through the cell; it is jelly like & contains many dissolved materials (oxygen, food, waste, etc) MITOCHONDRIA: produces the cell’s energy; it’s the site of cellular respiration, where food is combined with oxygen to release energy: Food + Oxygen --> Chemical Energy + Carbon Dioxide. NUCLEUS: controls the cell’s activities; usually found in the cell’s center & usually darker than the rest of the cell; it contains all the genetic information (DNA), which hold the directions for what the cell must do. VACUOLE: stores materials for the cell; is usually MUCH bigger in plant cells. Plant Vacuoles are huge. CELL WALL: supports and gives shape to plant cells; a rigid, non-living structure made of complex starch (cell walls are a major source of fiber). CHLOROPLAST: converts sun light to food in plant cells (photosynthesis); Light Energy + Carbon Dioxide --> Food + Oxygen Complex cells = more organelles LYSOSOME: digests food particles and wastes; can also digest cell parts and foreign invaders. RIBOSOME: makes proteins for the cell; tiny dot like structures . ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: allows materials to move through the cell; looks like flattened, folded pods. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE: controls what enters and leaves the nucleus. NUCLEOLUS: stores materials for the ribosomes; small, dark spot that may be seen in the nucleus; looks like a nucleus inside the nucleus. GOLGI APPARATUS: packages materials for transport; the Golgi apparatus receives chemicals from the endoplasmic reticulum.