* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - Weebly
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
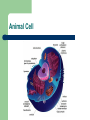
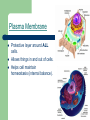
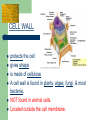
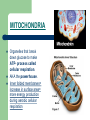
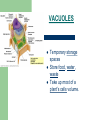
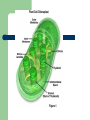
Cells www.teachersdomain.org Gallery of Cells Mrs. Harlin 1.1.1 Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. Animal Cell Plant Cell NUCLEUS Directs all cell activities Contains instructions for everything the cell does These instructions are found on a hereditary material called DNA Plasma Membrane Protective layer around ALL cells. Allows things in and out of cells. Helps cell maintain homeostasis (internal balance). CELL WALL protects the cell gives shape is made of cellulose A cell wall is found in plants, algae, fungi, & most bacteria. NOT found in animal cells. Located outside the cell membrane. MITOCHONDRIA Organelles that break down glucose to make ATP- process called cellular respiration. AKA the powerhouse. Inner folded membranes= increase in surface area= more energy production during aerobic cellular respiration VACUOLES Temporary storage spaces Store food, water, waste Take up most of a plant’s cells volume. Chloroplasts Green organelles that make food= photosynthesis found only in plant cells RIBOSOMES Site of protein synthesis! = to make proteins Float freely or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) In ALL cells! The Cell is like a Factory DNA from the nucleus codes for proteins. Proteins are used as enzymes for chemical reactions: – – – Energy production at the mitochondria Making glucose in the chloroplast Digesting large organic molecules Life’s Levels of Hierarchy Atoms-> Molecules-> Organelles-> Cells ->Tissues -> Organs -> Organ Systems -> Organisms This applies only for multicellular organisms.