* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objectives * To get an A grade I need to be able to:
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
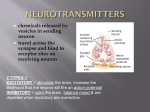
The Effect of Recreational Drugs in the Transmission Process in the Central Nervous System How do drugs affect your brain? Why does a cup of coffee wake you up, and aspirin stop your headache? Many drugs work by copying or blocking the effects of naturally occurring chemicals in your brain. What is a drug? • A drug is any chemical you take that affects the way your body works. Alcohol, caffeine, aspirin and nicotine are all drugs. A drug must be able to pass from your body into your brain. Once inside your brain, drugs can change the messages your brain cells are sending to each other, and to the rest of your body. They do this by interfering with your brain's own chemical signals: neurotransmitters that transfer signals across synapses. What is a synapse? • When a nerve impulse reaches the synapse at the end of a neuron, it cannot pass directly to the next one. Instead, it triggers the neuron to release a chemical neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter drifts across the gap between the two neurons. On reaching the other side, it fits into a tailor-made receptor on the surface of the target neuron, like a key in a lock. This docking process converts the chemical signal back into an electrical nerve impulse. Altering your mind? • • Some drugs interfere with neurotransmitters in the brain. These 'mind-altering' drugs change our interpretation of the world, our behaviour, and our mood. For example, cannabis affects neurons releasing acetylcholine, noradrenaline and dopamine. LSD is a combination of an artificial acid and a natural molecule found in the fungus Claviceps purpurea (Ergot). LSD mimics serotonin action in the brain, which seems to explain its hallucinogenic effects. What makes drugs addictive? • Doctors call a drug addictive if it makes you dependent on the drug. Unpleasant withdrawal symptoms appear unless you take the drug. Addictive drugs also make you crave them - you have an overwhelming urge to continue taking the drug, even after withdrawal symptoms have disappeared. Reward Pathway: Where pleasure overrides other drives. Why are some drugs addictive? • Scientists think that all addictive drugs activate the brain's 'reward system', by increasing the release of the chemical dopamine from neurons in key areas of the brain. Dopamine release occurs after pleasurable experiences, for example after food or exercise. Drugs that artificially increase dopamine release in this way may cause craving for more. It is possible that some people may have a genetic tendency to make them develop drug addictions extremely rapidly. Dopamine releasing neurons Classwork • • • • Research the mode of action on the CNS of one of the drugs below. Nicotine Cocaine Cannabis Links to Issues and Debates Ethics-Most research into the effects of drugs comes from animal studies. Strengths and weaknesses? Reductionism Nature-nurture The use of psychological knowledge within society – e.g. understanding causes in order to deal with them. Can you identify where the issues and debates were in today’s lesson??????? Evaluate: Arguments About their Effects on Transmission. Strengths Weaknesses There is plenty of research: It is reductionist: The use of animals in research: Credibility: The use of brain scanning: