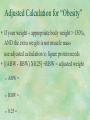* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download protein - CSU, Chico
Index of biochemistry articles wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
PROTEIN-Part Two NFSC 303 – Nutrition and Fitness McCafferty Protein RDA Nitrogen Balance Studies: N Balance = Intake: Output: Example: On the RDA table: Males 19-24 years: (based on reference male 5’10” 160# ) Females 19-24 years: (based on reference female 5’5” 128#) “Appropriate Body Weight” Females: 100# for first 5’ of height, plus _______ __________________________________________ Males: 106# for first 5’ of height, plus _________ __________________________________________ (for those under 5’, subtract 2 lb. per inch under 5’) Use appropriate body weight to calculate your protein needs Adjusted Calculation for “Obesity” If your weight appropriate body weight > 130%, AND the extra weight is not muscle mass use adjusted calculation to figure protein needs [(ABW - RBW) X0.25] +RBW = adjusted weight ABW = RBW = 0.25 = Example: Deb is 5’7” tall and weighs 185 pounds. She is lightly to moderately active. Calculate her protein needs. Typical U.S. Intake Typical Male: Typical Female: Older Americans may need Do Athletes need more protein? Do Athletes require protein supplements? Protein Requirements for Exercisers/Athletes Regular exerciser: No RDA for athletes, but recommended: Endurance Strength (resistance trained) Vegetarian: Controversial – Protein sparing effect of adequate kcals Example 1: Regular exerciser Beth cycles 4-5 hours per week. She’s 5’8” tall and weighs 145 pounds. Estimate her protein needs. Example 2: Strength Athlete Mike is a competitive body builder . He is 6’1” tall and weighs 205#. Estimate his protein needs. Excessive Protein Intake >2.0g/kg? ASSOCIATED WITH: No evidence to support kidney damage in healthy adults. Vegetarianism Affects protein intake because some or all animal foods are eliminated from the diet. Why Do People Go Veggie? Potential for improved health Environmental Concerns Concern over inhumane treatment of animals Cultural or Religious Practices Scarce availability or high cost of meat Some combination of these The Vegetarian Continuum Vegetarian: The Vegetarian Continuum The Vegetarian Continuum Other terms: Far vegetarian: Pescovegetarian: Semivegetarian: Fruitarian: But are there health benefits? Vegetarian diet is usually: Vegetarians Are At Decreased Risk For: Colon Cancer Hypertension Gallstones Kidney Stones Vegetarians also drink less alcohol are less likely to smoke are less likely to use drugs exercise more lead a healthier lifestyle overall Plants Do Provide Protein! Quick Review: Proteins are built from amino acids In order for the body to build a protein, it must have ALL the EAAs. If just one essential amino acid is missing, protein cannot be synthesized, and all the other amino acids are deaminated. But all protein sources are not created equal. Complete Proteins • meat, fish and poultry • eggs • dairy “Incomplete” proteins So, how does the body make protein from plant foods? By combining “Complimentary Proteins” Complimentary proteins: protein foods whose AAs compliment each other so that the EAAs missing from each are supplied by the other. For Example: So … Even better: Peanut-sesame seed snack mix minestrone soup and salad topped with nuts grain and nut cereal with soy milk add cheese to bean and rice burrito macaroni and cheese add hard-cooked egg to salad drink a glass of milk with the meal A Quick Word About Soy Protein Potential Nutritional Concerns With a Vegetarian Diet Variety and Adequacy The more restrictive the diet, the more potential for nutritional inadequacy Special attention to combining proteins: Specific Nutrients of Concern Calcium Iron and Zinc Vitamin B12 Vitamin D Vegetarian Sources Calcium Iron Vegetarian Sources Vitamin B12 Vitamin D Choose Wisely Choose whole grains Choose a variety of fruits and vegetables Choose plenty of legumes Combine protein sources every day Watch the junk food! Fat, saturated fat, cholesterol, and empty calories